Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2013; 19(28): 4582-4589
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4582
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4582
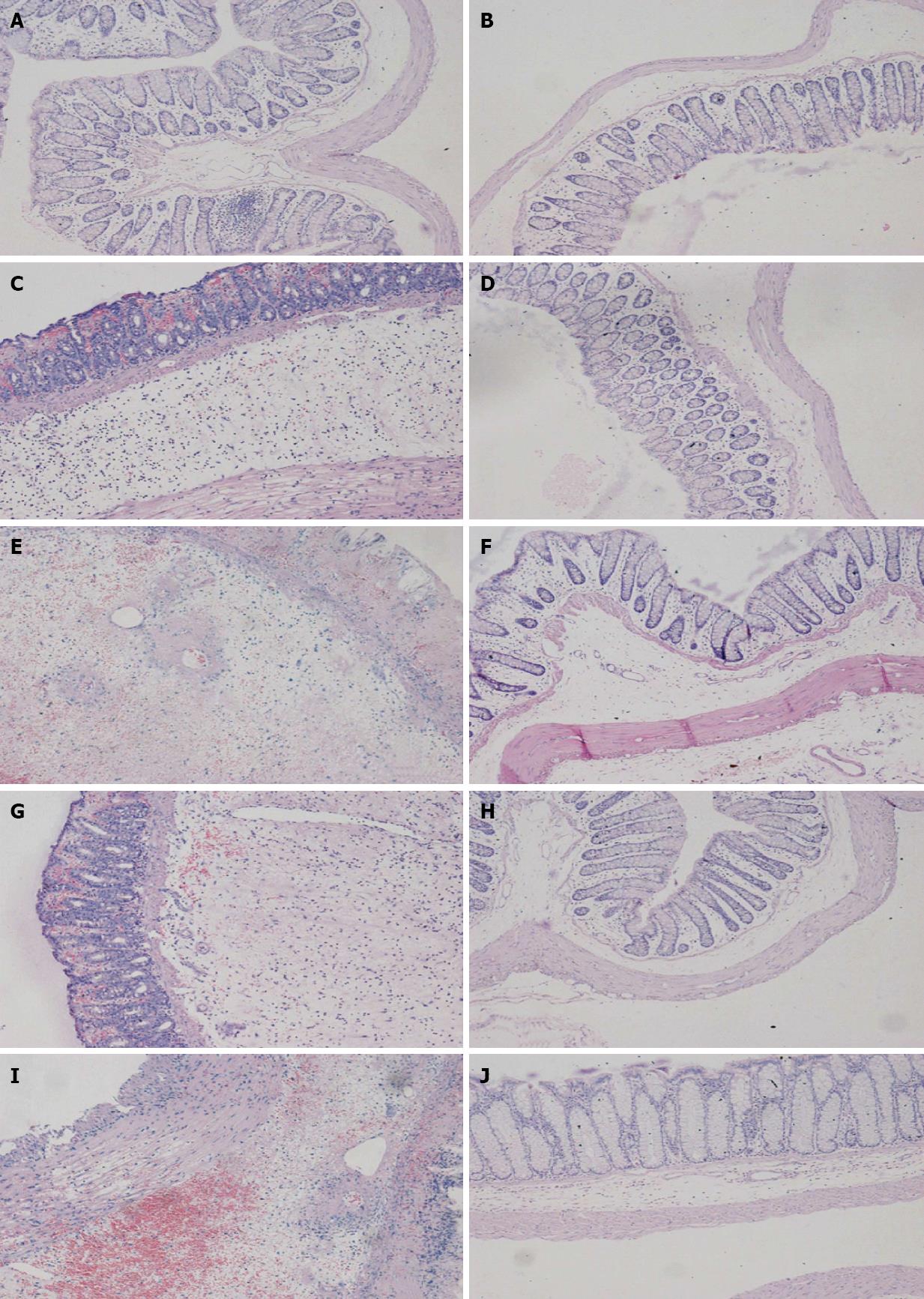
Figure 1 Photomicrographs (hematoxylin and eosin stain, × 100) of distal colon at 2 and 7 d, respectively.
A, B: Control group; C, D: Placebo group; E, F: Berberine group; G, H: Aminoguanidine group; I, J: Berberine + aminoguanidine group. At 2 d, histological inflammatory features including mucosal hemorrhage, submucosal edema, and inflammatory infiltration in the lamina propria and the submucosa were observed in the placebo, berberine, aminoguanidine, and berberine + aminoguanidine groups (A, C, E, G, I). At 7 d, there was no marked inflammatory feature compared with the control group (B, D, F, H, J).
- Citation: Tang QL, Lai ML, Zhong YF, Wang AM, Su JK, Zhang MQ. Antinociceptive effect of berberine on visceral hypersensitivity in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(28): 4582-4589
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i28/4582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4582