Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 4031-4038
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4031
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4031
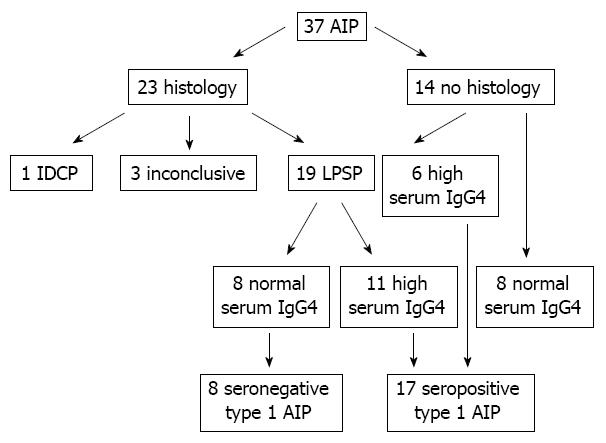
Figure 1 Enrolled patients and classification of autoimmune pancreatitis.
Among 37 patients with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), one case was type 2 AIP and 19 patients were type 1 AIP by histology. The pathological diagnosis was inconclusive in three cases among 23 tissue samples. Among 14 patients without histology, eight patients were excluded because of normal serum immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) levels. Ultimately, 25 patients with definite type 1 AIP (19 histologically and six serologically diagnosed cases) were enrolled in this study. LPSP: Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis; IDCP: Idiopathic duct-centric chronic pancreatitis.
- Citation: Paik WH, Ryu JK, Park JM, Song BJ, Park JK, Kim YT, Lee K. Clinical and pathological differences between serum immunoglobulin G4-positive and -negative type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 4031-4038
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/4031.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4031