Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 3980-3989
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3980
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3980
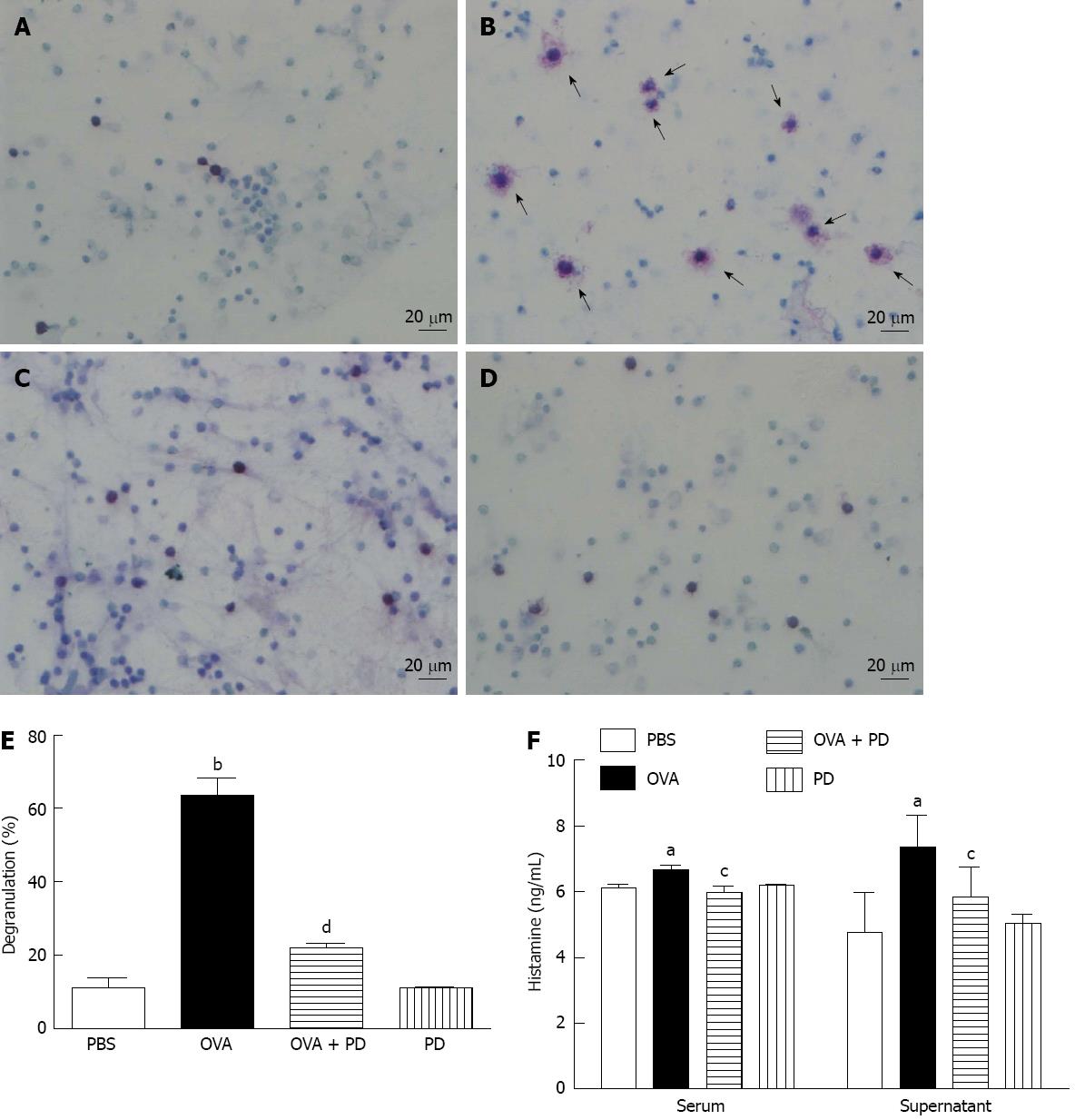
Figure 5 Polydatin therapy reduced mast cell degranulation and activation.
A: Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) group; B: Ovalbumin (OVA) group; C: OVA + polydatin (PD) group; D: PD group; E: Degranulated mast cells were counted from at least 500 total cells and the percentage of degranulation was calculated as degranulated cells against total cells; F: The release of histamine in serum (left panel), rat small intestine tissue, or peritoneal lavage solution (right panel) was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. n = 8, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs PBS group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs OVA group. The mast cells in rat small intestine tissue or peritoneal lavage solution were identified by toluidine blue stain. Mast cells were considered degranulated if at least 5 granules appeared outside the cell body. Arrows indicate degranulated mast cells (magnification, × 250).
-
Citation: Yang B, Li JJ, Cao JJ, Yang CB, Liu J, Ji QM, Liu ZG. Polydatin attenuated food allergy
via store-operated calcium channels in mast cell. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 3980-3989 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/3980.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3980