Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 3969-3979
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969
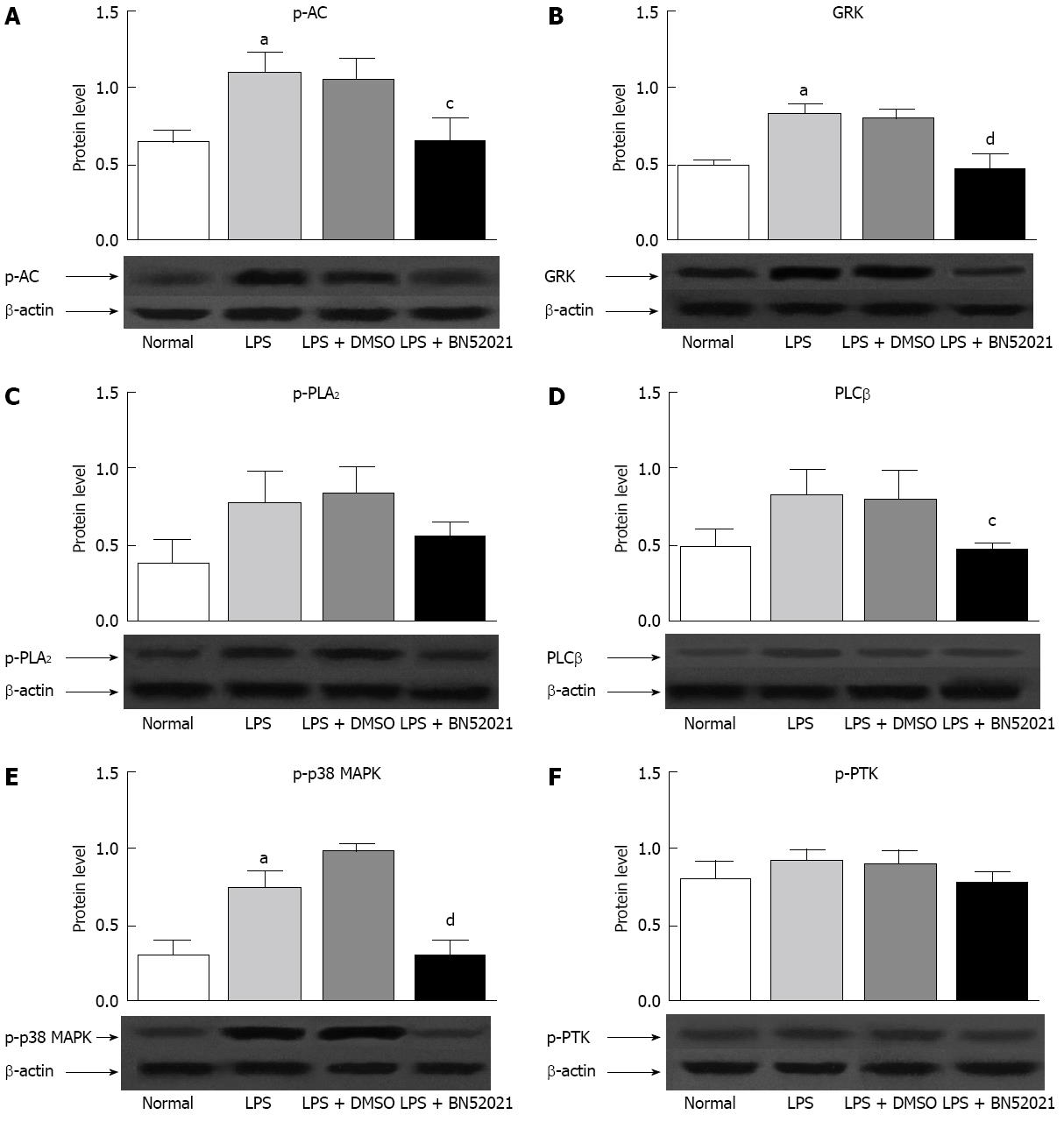
Figure 4 The effect of BN52021 on platelet-activating factor receptor signaling molecules at the protein level under lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.
The protein level of p-adenylate cyclase (p-AC) (A), G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRK) (B), p-phospholipase A2 (p-PLA2) (C), phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) (D) and p-p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (p-p38 MAPK) (E) was up-regulated after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation vs the blank control (aP < 0.05). The up-regulation of p-AC, p-p38 MAPK, GRK and PLCβ protein levels was significantly suppressed by BN52021. However, p-PLA2 and phosphorylated protein tyrosine kinase (p-PTK) protein levels were insignificantly up-regulated after LPS stimulation and were not significantly changed by BN52021 (F). cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs LPS + dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) groups.
- Citation: Xia SH, Xiang XH, Chen K, Xu W. Roles of BN52021 in platelet-activating factor pathway in inflammatory MS1 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 3969-3979
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/3969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969