Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
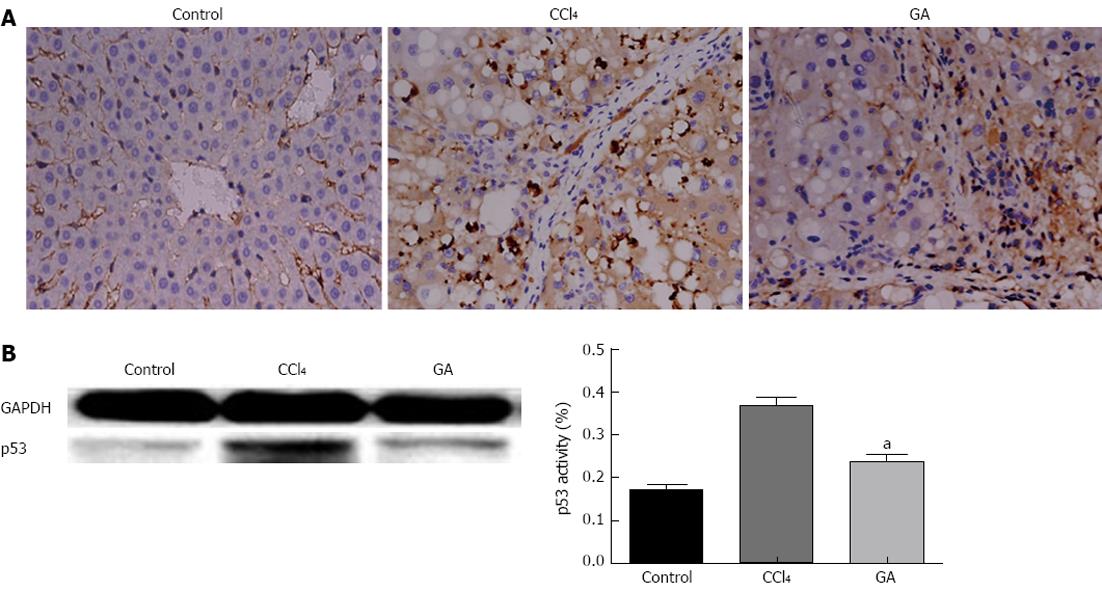
Figure 3 Effect of glycyrrhizic acid treatment on the expression level of p53 in the livers of rats injured by carbon tetrachloride.
A: Liver tissue slices from the different groups were subjected to immunohistochemistry (original magnification, × 400). B: Total protein fractions prepared from livers were analyzed by Western blotting to assess the expression level of p53 and GAPDH to confirm the same sample loading. The results of Western blotting analysis were similar in at least three replicate independent experiments. All values are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was defined as follows: aP < 0.05 vs the carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) group. GA: Glycyrrhizic acid.
-
Citation: Guo XL, Liang B, Wang XW, Fan FG, Jin J, Lan R, Yang JH, Wang XC, Jin L, Cao Q. Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats
via a p53-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i24/3781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781