Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
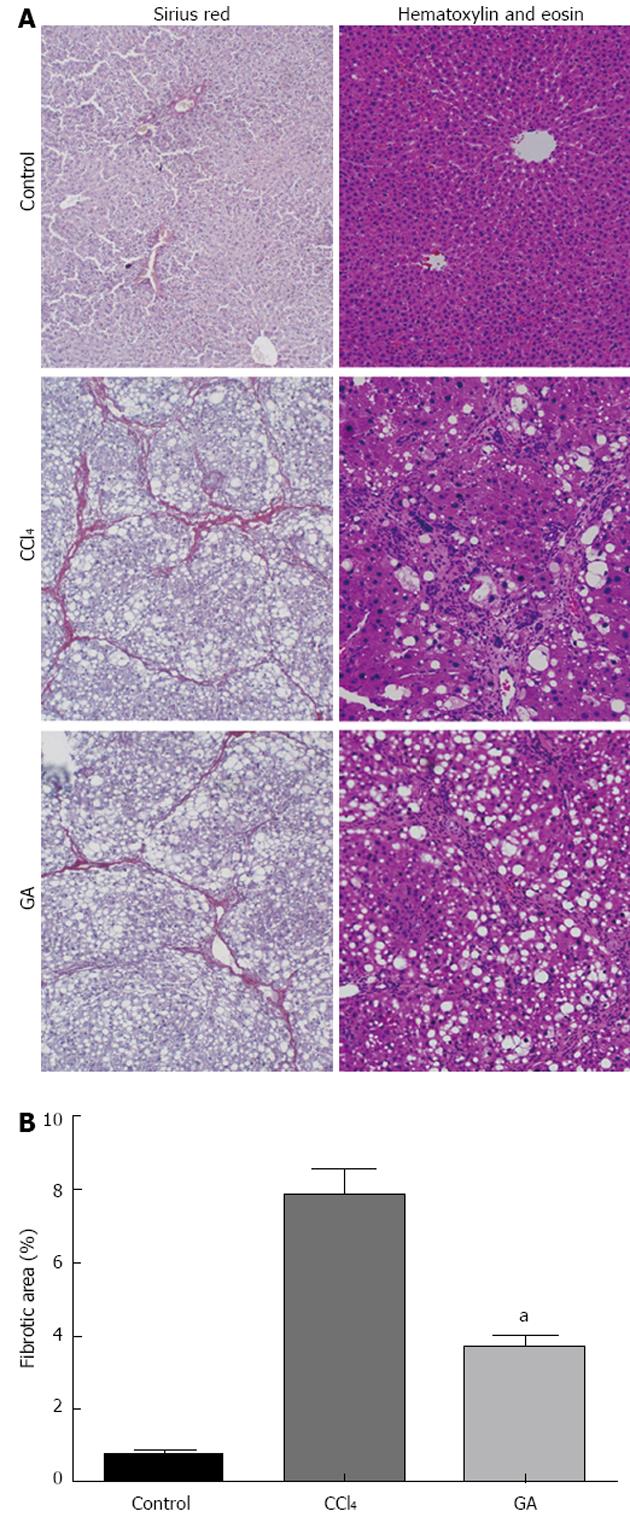
Figure 1 Histological examination of liver by hematoxylin and eosin and Sirius red staining.
A: Histological examination. Rats were treated with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and/or glycyrrhizic acid (GA). Liver tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin or Sirius red (original magnification, × 100); B: Quantitative analysis of liver fibrosis by Sirius red staining. Results are represented as fibrotic area (%), which signifies the proportion of area stained red/area of total area-vascular lumen. Values are mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs CCl4.
-
Citation: Guo XL, Liang B, Wang XW, Fan FG, Jin J, Lan R, Yang JH, Wang XC, Jin L, Cao Q. Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats
via a p53-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i24/3781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781