Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2013; 19(24): 3770-3780
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3770
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3770
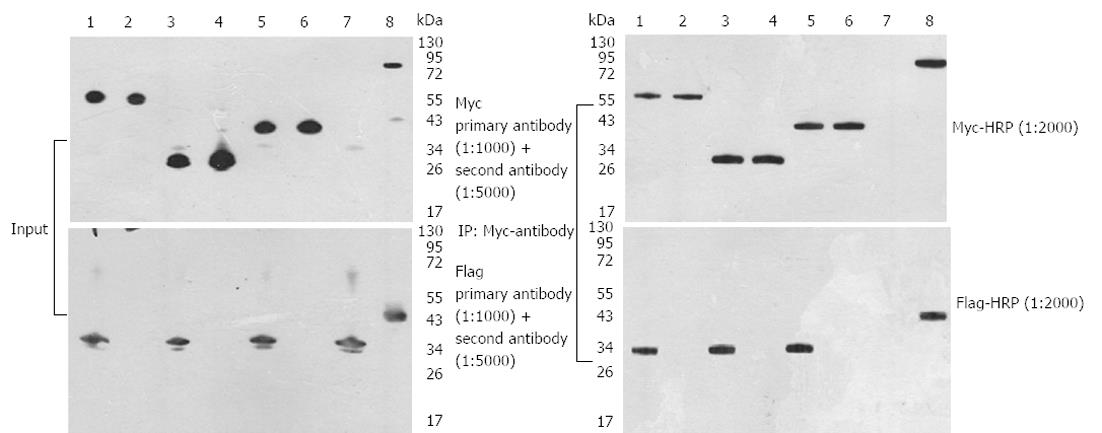
Figure 5 Expression and interaction of 14-3-3, potassium channel modulatory factor 1, quinone oxidoreductase, hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase and 14-3-3plasmids in HEK 293FT cells.
A: Expression of the 14-3-3σ, potassium channel modulatory factor 1 (KCMF1), quinone oxidoreductase (NQO2), hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase (HIBADH) plasmids. HEK 293FT cells were transfected with different plasmids. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, the cells were lysed, and Western blotting analysis was performed with an anti-Myc or anti-Flag antibody (1:1000); B: Interaction of 14-3-3σ and KCMF1, NQO2 or HIBADH. HEK 293FT cells were transfected with different plasmids. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, the cells were lysed and immunoprecipitations were performed with an anti-Myc antibody (1:2000). After the proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, immunoblot analysis was performed with antibodies against Flag protein (1:2000). 1: Sample 1 KCMF1; 2: Negative Control-1; 3: Sample 2 NQO2; 4: Negative Control-2; 5: Sample 3 HIBADH; 6: Negative Control-3; 7: Negative Control-4; 8: Positive.
- Citation: Zou J, Mi L, Yu XF, Dong J. Interaction of 14-3-3σ with KCMF1 suppresses the proliferation and colony formation of human colon cancer stem cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(24): 3770-3780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i24/3770.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3770