Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2013; 19(22): 3385-3396
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385
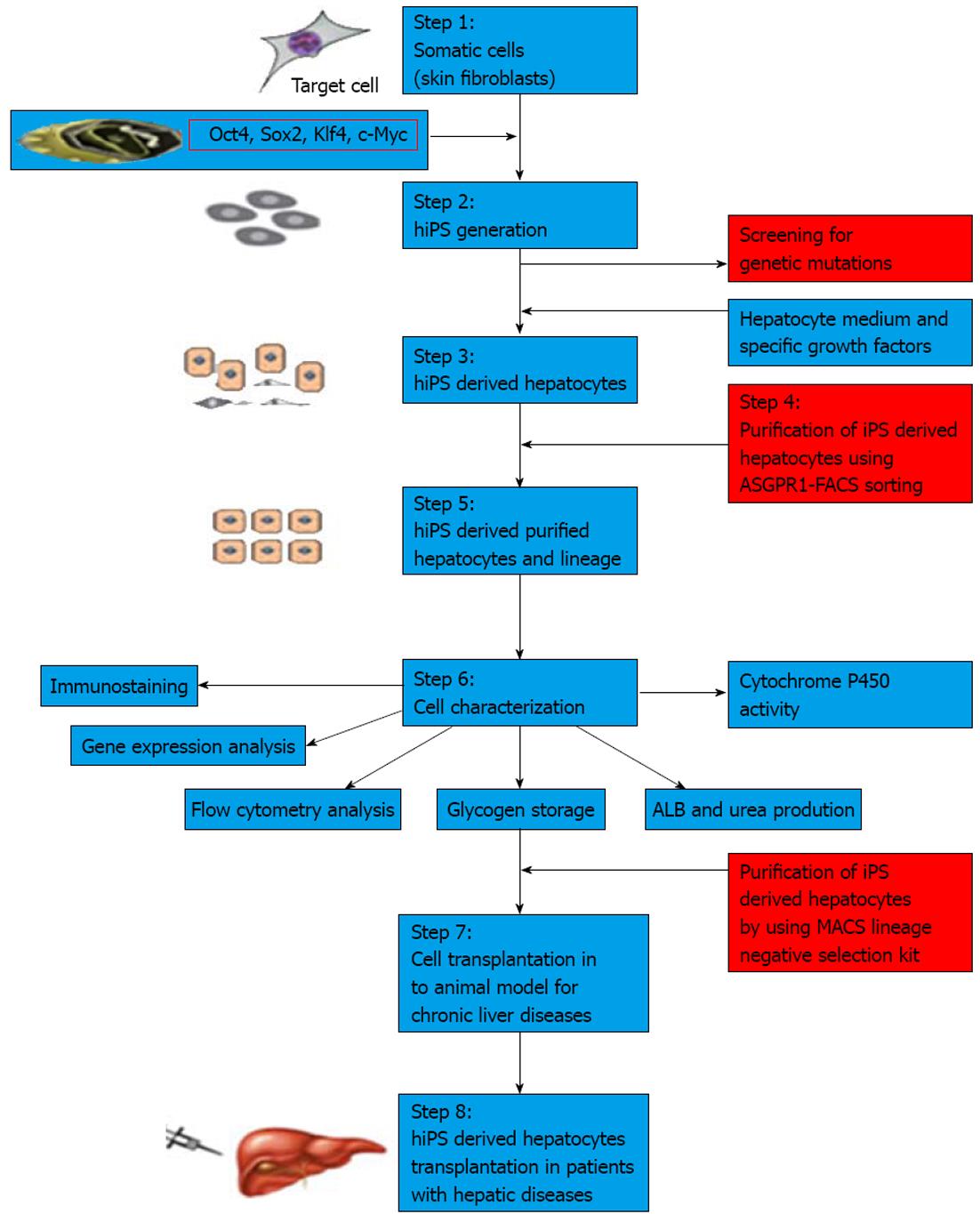
Figure 2 Flow diagram showing the strategy for human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte clinical applications.
Steps 1 and 2, human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are generated from somatic cells using reprogramming techniques and screened for mutations; Step 3, hiPSCs are differentiated into hepatocytes using specific growth factors and medium; Step 4, enrichment of hiPSC-derived hepatocytes; Steps 5 and 6, characterization of enriched iPSC-derived hepatocytes for protein expression, gene expression and functional assays. Before clinical transplantation, hiPSC-derived hepatocytes are enriched again using negative selection against pluripotent cells to avoid teratoma formation; Step 7, transplantation of enriched hiPSC-derived hepatocytes into chronic liver failure animal model; Step 8, hiPSC-derived enriched hepatocytes could be transplanted into liver disease patients. Oct: Octamer-binding transcription factor; Sox2: SRY box-containing gene 2; Klf4: Kruppel-like factor 4; ASGPR: Asialoglycoprotein receptor; FACS: Fluorescence activated cell sorting; MACS: Magnetic-activated cell sorting; ALB: Albumin.
- Citation: Rao MS, Sasikala M, Reddy DN. Thinking outside the liver: Induced pluripotent stem cells for hepatic applications. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(22): 3385-3396
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i22/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385