Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2013; 19(22): 3385-3396
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385
Published online Jun 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385
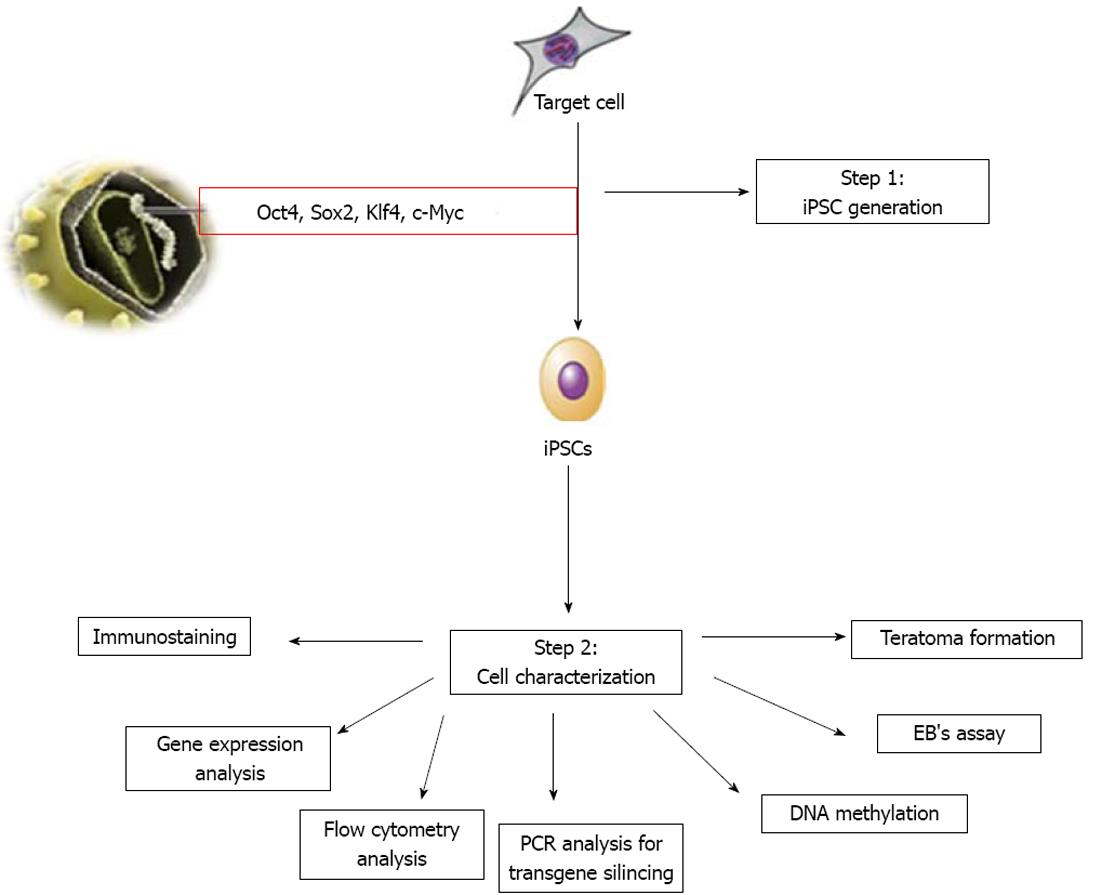
Figure 1 Flow diagram of generation and characterization of human induced pluripotent stem cells.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are derived through the introduction of stem cell factors into fibroblasts. After that, assessment of pluripotency of iPSCs can be studied by expression of protein and genes using various techniques such as immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods, respectively. In vitro and in vivo differentiation ability of iPSCs can be studied by embryoid body assay (EB assay) and teratoma formation assay, respectively. In addition, PCR analysis is required to demonstrate silencing of transgene expression in iPSCs and DNA methylation to confirm reprogramming of somatic cells. Oct: Octamer-binding transcription factor; Sox2: SRY box-containing gene 2; Klf4: Kruppel-like factor 4.
- Citation: Rao MS, Sasikala M, Reddy DN. Thinking outside the liver: Induced pluripotent stem cells for hepatic applications. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(22): 3385-3396
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i22/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3385