Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2013; 19(21): 3324-3331
Published online Jun 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3324
Published online Jun 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3324
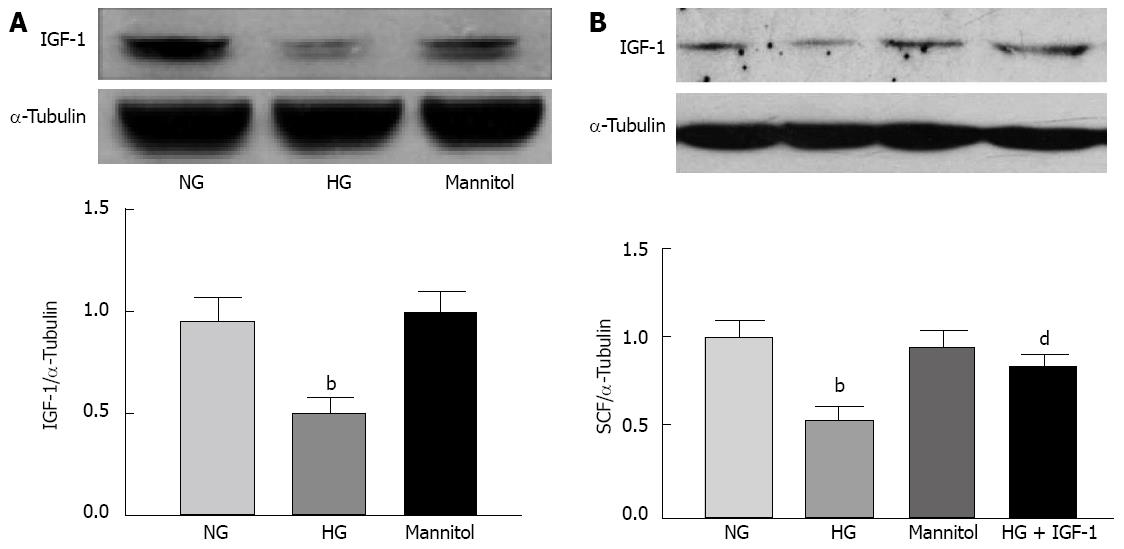
Figure 5 High glucose inhibited endogenous insulin-like growth factor-1 and stem cell factor expression.
A: Expression of endogenous insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in SMCs cultured in a high glucose (HG) medium for 24 h. bP < 0.01 vs the normal glucose (NG) group; B: Stem cell factor (SCF) expression in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) exposed to HG, and effects of the addition of exogenous IGF-1 (100 ng/mL). bP < 0.01 vs the NG group; and dP < 0.01 vs HG group. The Western blotting are representatives of 4 independent experiments. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control (each bar represents the mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments).
- Citation: Wang Y, Xu XY, Tang YR, Yang WW, Yuan YF, Ning YJ, Yu YJ, Lin L. Effect of endogenous insulin-like growth factor and stem cell factor on diabetic colonic dysmotility. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(21): 3324-3331
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i21/3324.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3324