Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2013; 19(20): 3161-3164
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3161
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3161
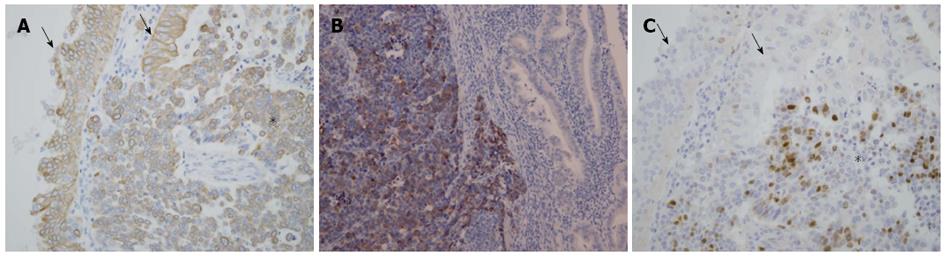
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry for cytokeratin 19, synaptophysin, and Ki-67.
A: Both the solid (asterisk) and papillary (arrows) components were positive for CK19. Magnification: × 200; B: Synaptophysin expression was evident in the solid component (left), indicating a neuroendocrine tumor, but not in the papillary component (right). Magnification: × 100; C: Although Ki-67-positive cells were scarce in the papillary component (arrows), many Ki-67-positive cells were identified in the solid component (asterisk). Magnification: × 200.
- Citation: Onishi I, Kitagawa H, Harada K, Maruzen S, Sakai S, Makino I, Hayashi H, Nakagawara H, Tajima H, Takamura H, Tani T, Kayahara M, Ikeda H, Ohta T, Nakanuma Y. Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct accompanying biliary mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(20): 3161-3164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i20/3161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3161