Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2013; 19(20): 3027-3042
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027
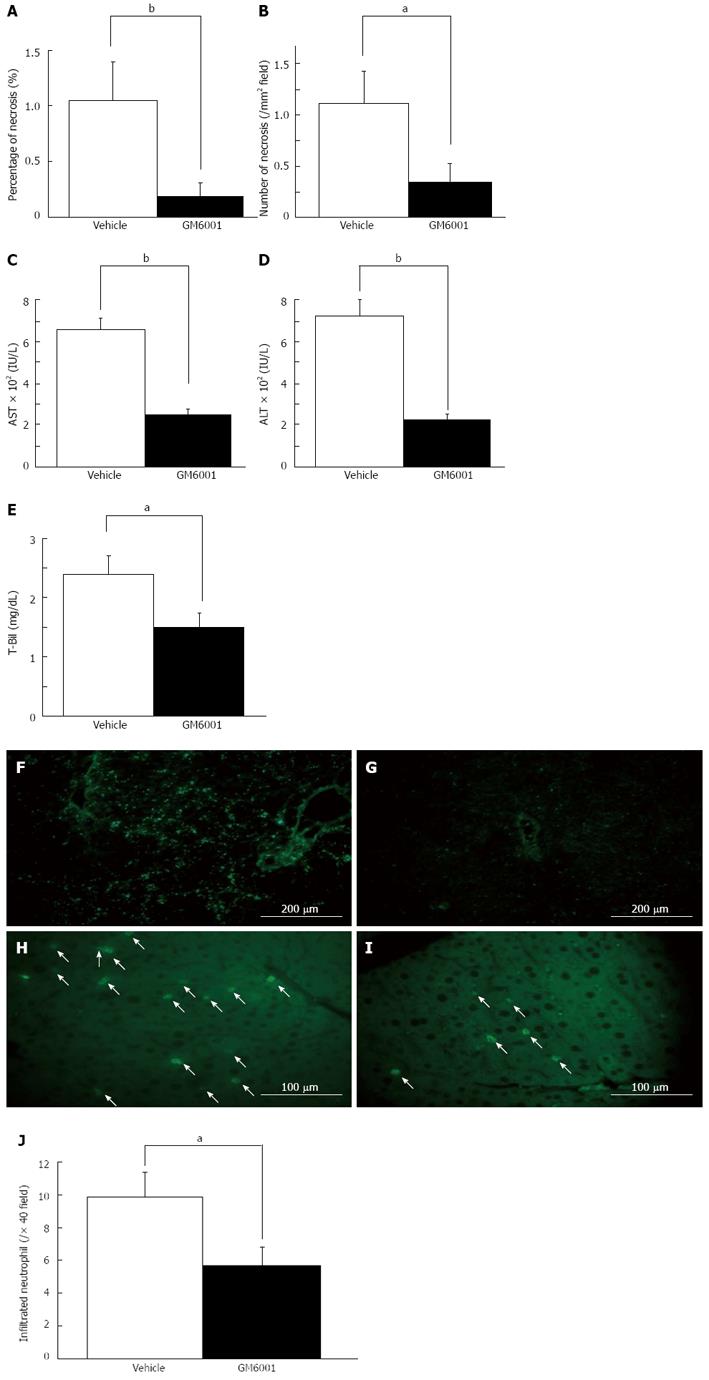
Figure 9 Broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor GM6001 ameliorate initial injury of the liver 6 h after 80%-partial hepatectomy.
We inhibited matrix metalloproteinase-9 by GM6001 in 80%-partial hepatectomy (PH) mice, and determined liver necrosis 6 h after 80%-PH. Liver damage was significantly reduced in the GM6001-treated mice compared with that in the vehicle-treated group (A, B). Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (C), alamine aminotransferase (ALT) (D) and total bilirubin (T-Bil) (E) were significantly lower in the GM6001-treated mice than those in the vehicle-treated mice. Representative images of in situ gelatin zymography analysis with DQ gelatin are shown. Gelatinolytic activity was suppressed in the GM6001-treated mice (G) compared with that in the vehicle-treated mice (F). Representative images of myeloperoxidase staining on remnant liver (RL) sections in vehicle-treated mice (H) and GM6001-treated mice (I) are shown. A histogram of the number of accumulated neutrophils in the RL after extended hepatectomy shows that there are significantly fewer neutrophils in the GM6001-treated mice than in the vehicle-treated mice (J) (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated mice).
- Citation: Ohashi N, Hori T, Chen F, Jermanus S, Nakao A, Uemoto S, Nguyen JH. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the initial injury after hepatectomy in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(20): 3027-3042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i20/3027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027