Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2013; 19(20): 3027-3042
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027
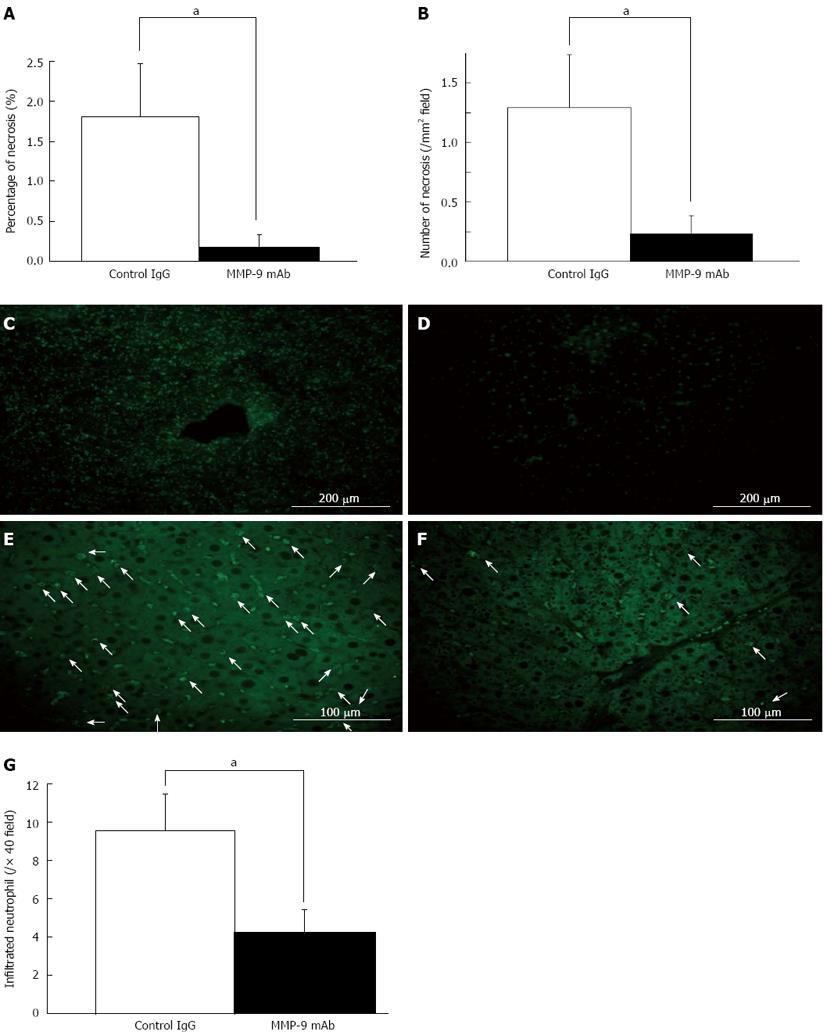
Figure 8 Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by a monoclonal antibody of matrix metalloproteinase-9.
We investigated the outcome of inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by monoclonal antibody (mAb) in 80%-partial hepatectomy (PH) in mice, and performed histological analysis of liver necrosis 6 h after 80%-PH (A, B). Liver damage was significantly reduced in the group with mAb compared with that in the control IgG group. Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alamine aminotransferase and total bilirubin were lower in the mAb-treated mice, but this was not significant. Representative images of in situ gelatin zymography analysis with DQ gelatin revealed that gelatinolytic activity was suppressed in the mAb-treated mice (D) compared with that in control IgG-treated mice (C). Representative images of myeloperoxidase staining on remnant liver (RL) sections in control IgG-treated mice (E) and mAb-treated mice (F) are shown. A histogram of the number of accumulated neutrophils in the RL 6 h after 80%-PH shows that there are significantly fewer neutrophils in mAb-treated mice than in IgG-treated controls (G) (aP < 0.05 vs IgG group).
- Citation: Ohashi N, Hori T, Chen F, Jermanus S, Nakao A, Uemoto S, Nguyen JH. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the initial injury after hepatectomy in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(20): 3027-3042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i20/3027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3027