Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2013; 19(20): 3007-3017
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3007
Published online May 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3007
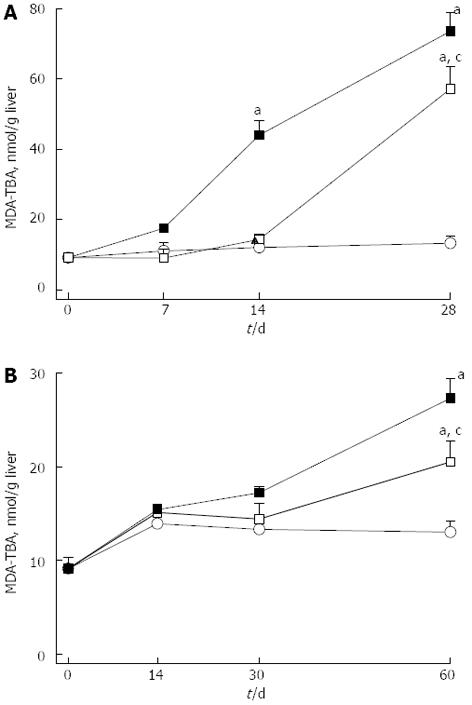
Figure 2 Concentrations of malondialdehyde-thiobarbituric acid reactive substances.
A: Liver of rat fed a choline-deficient diet; B: Liver of rat fed a high fat diet. Closed square: Without; open square: With Realsil administration; open circle: Control rats fed a standard chow-diet with adequate content of choline. Data are mean ± SD of n = 5 rats per group at each time point. aP < 0.05 vs control rats; cP < 0.05 vs untreated rats at the same time points. MDA-TBA: Malondialdehyde-thiobarbituric.
- Citation: Grattagliano I, Diogo CV, Mastrodonato M, de Bari O, Persichella M, Wang DQ, Liquori A, Ferri D, Carratù MR, Oliveira PJ, Portincasa P. A silybin-phospholipids complex counteracts rat fatty liver degeneration and mitochondrial oxidative changes. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(20): 3007-3017
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i20/3007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3007