Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2013; 19(19): 2904-2912
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904
Published online May 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904
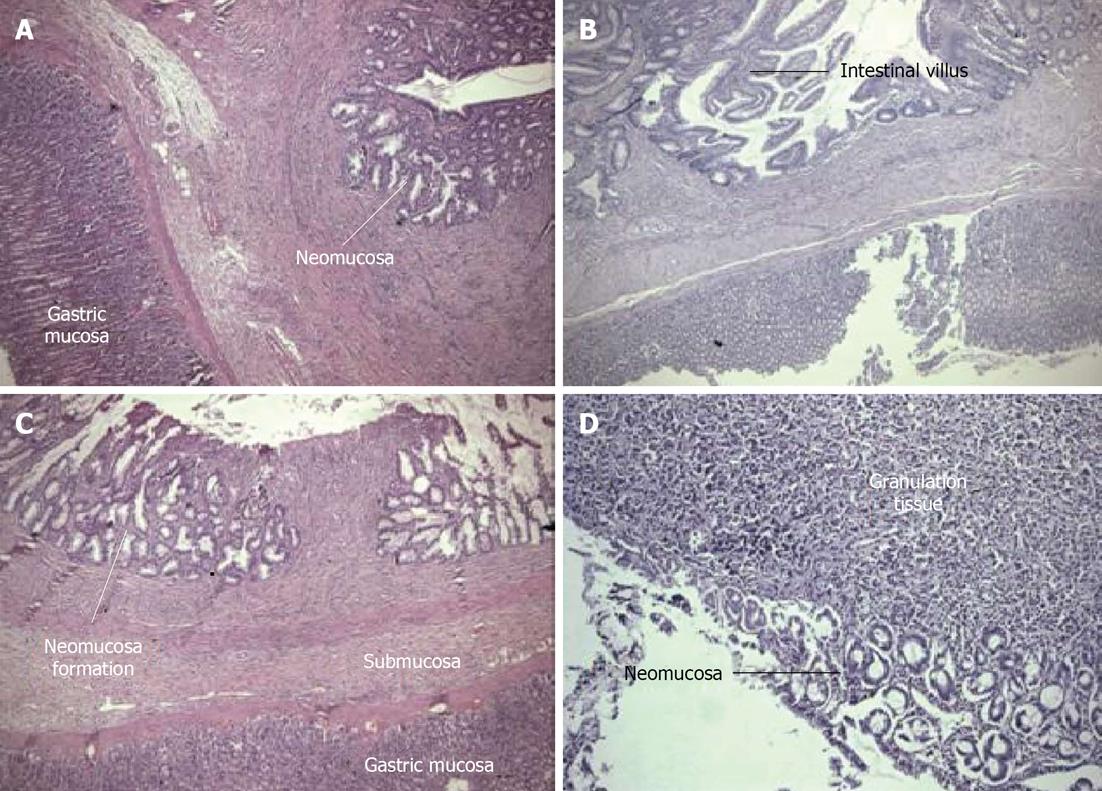
Figure 3 There were significant differences in the villus density in all of the groups compared with the control group.
A: Gastric corpus mucosa on the left, newly formed thin neomucosa on the right. The muscularispropria has not yet formed. The granulation tissue regressed [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) × 100] (Group 3); B: Neomucosa formation is observed at the bottom of the gastric mucosa (HE × 125) (Group 4); C: The granulation tissue is in the middle, with newly formed neomucosa on either side. At the bottom, the stomach tissue is visible (HE x 100) (Group 2); D: The early development of the mucosal layer and granulation tissue (HE x 125) (Group 1).
- Citation: Adas G, Adas M, Arikan S, Sarvan AK, Toklu AS, Mert S, Barut G, Kamali S, Koc B, Tutal F. Effect of growth hormone, hyperbaric oxygen and combined therapy on the gastric serosa. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(19): 2904-2912
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i19/2904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2904