Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2013; 19(18): 2761-2771
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2761
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2761
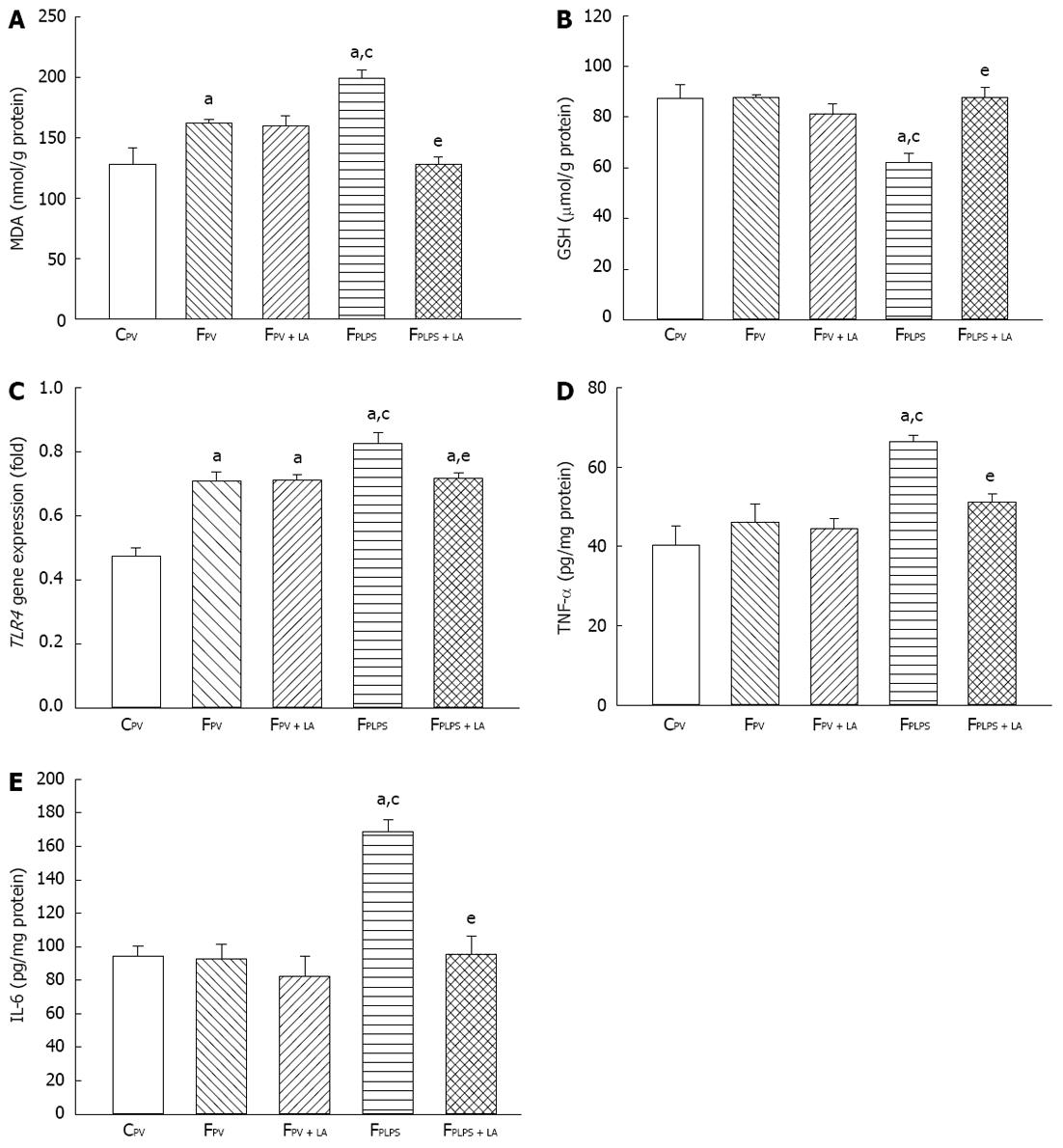
Figure 2 Effect of α-lipoic acid on portal endotoxemia-induced changes in hepatic oxidative and inflammatory markers.
The following parameters were measured from liver of each group of fructose-fed rats and the control group: (A) Malondialdehyde (MDA) content; (B) Glutathione (GSH) content; (C) Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene expression; (D) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) protein; and (E) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) protein. Values are expressed as mean ± SE, n = 6 per group. aP < 0.05 vs CPV; cP < 0.05 vs FPV; eP < 0.05 vs FPLPS. C: Regular diet; F: High-fructose enriched diet; LA: Lipoic acid; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides.
- Citation: Tian YF, He CT, Chen YT, Hsieh PS. Lipoic acid suppresses portal endotoxemia-induced steatohepatitis and pancreatic inflammation in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(18): 2761-2771
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i18/2761.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2761