Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2013; 19(15): 2319-2330
Published online Apr 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2319
Published online Apr 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2319
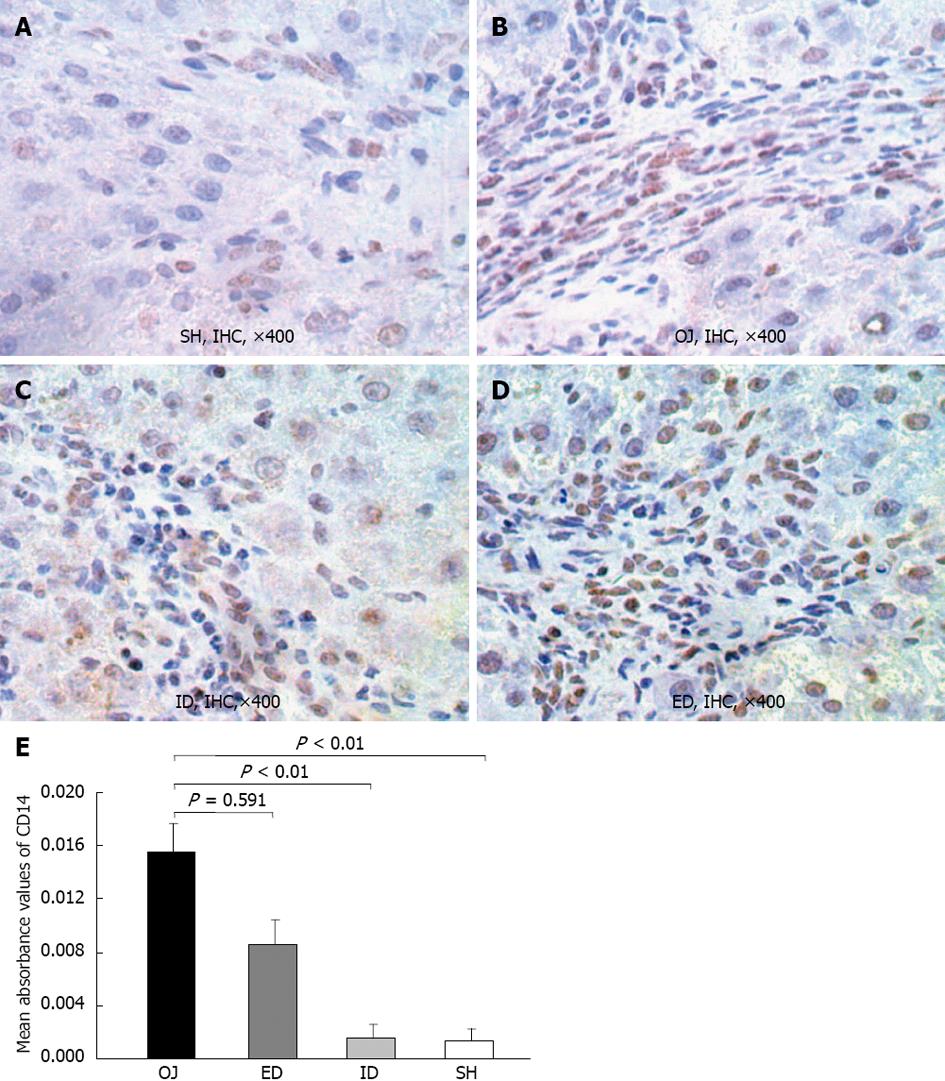
Figure 5 Representative immunohistochemical analysis of CD14 in rat liver tissues of sham operation, obstructive jaundice, internal and external biliary drainage groups.
A: CD14-immunoreactivity was detected mainly in the membrane of Kupffer cell on the edge of liver sinusoid and portal areas. There was slight expression of CD14 in sham operation (SH) rats; B: 14 d after bile duct ligation, the CD14-immunoreactivity became stronger as compared to SH rats; C: After relief of obstructive jaundice (OJ) by internal biliary drainage (ID), the expression of CD14 was markedly suppressed; D: The expression of CD14 in external biliary drainage (ED) rats was still at a high level; E: Comparison of mean absorbance values of CD14 in liver tissues among the four groups. IHC: Immunohistochemical.
- Citation: Wang ZK, Xiao JG, Huang XF, Gong YC, Li W. Effect of biliary drainage on inducible nitric oxide synthase, CD14 and TGR5 expression in obstructive jaundice rats. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(15): 2319-2330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i15/2319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2319