Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2013; 19(14): 2270-2277
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2270
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2270
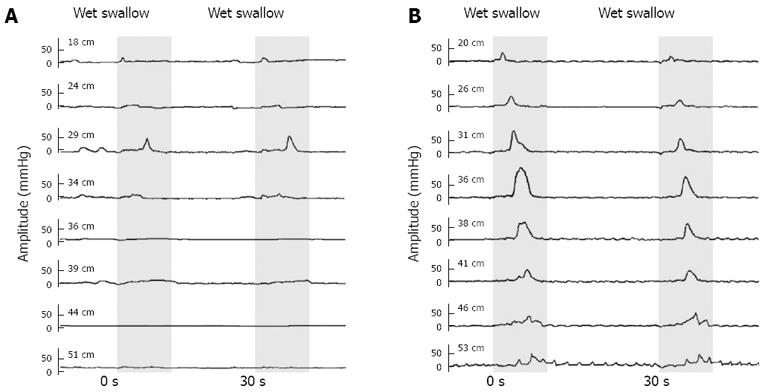
Figure 4 Manometric tracings of a fast-eating non-cardiac chest pain patient diagnosed with ineffective esophageal motility before (A) and after (B) 6-mo gum-chewing exercise.
The numbers (in cm) on the left indicate the distances from the nose to each side-hole on the catheter.
- Citation: Li KL, Chen JH, Zhang Q, Huizinga JD, Vadakepeedika S, Zhao YR, Yu WZ, Luo HS. Habitual rapid food intake and ineffective esophageal motility. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(14): 2270-2277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i14/2270.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2270