Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2013; 19(14): 2249-2255
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249
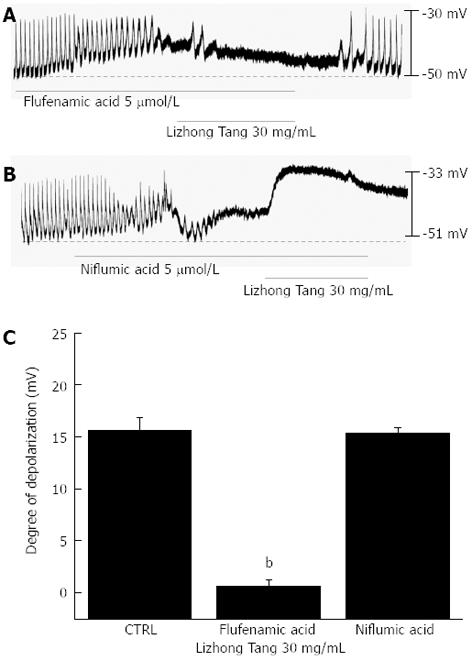
Figure 2 Effects of flufenamic acid (a nonselective cation channel blocker) or niflumic acid (a Cl- channel blocker) on Lizhong Tang-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestines.
A: The application of flufenamic acid (5 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, and in the presence of flufenamic acid, Lizhong Tang (30 mg/mL) did not cause membrane depolarization; B: In contrast, although niflumic acid (5 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, it did not block Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; C: The responses to Lizhong Tang in the presence of flufenamic acid or niflumic acid are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs control group. CTRL: Control.
- Citation: Hwang MW, Kim JN, Song HJ, Lim B, Kwon YK, Kim BJ. Effects of Lizhong Tang on cultured mouse small intestine interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(14): 2249-2255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i14/2249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249