Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2013; 19(14): 2162-2170
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2162
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2162
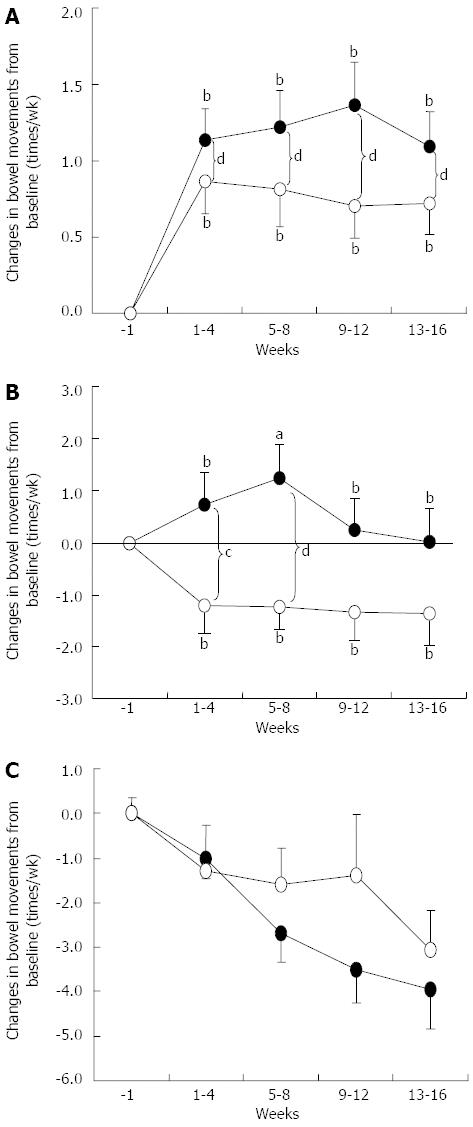
Figure 3 Effects of BB536 intake on changes in defecation frequency.
A: Subgroup of patients with low infrequent defecation (≤ 4 times a week); B: Subgroup of patients with normal frequency of defecation (5-9 times a week); C: Subgroup of patients with high frequency of defecation (≥ 10 times a week) at baseline (week-1). Results present the summary of Trials 1 and 2 for the placebo (○) and BB536 groups (●) composed of the BB536 group in Trial 1 and BB536-H and BB536-L groups in Trial 2). Times of defecation were averaged weekly for each individual, and changes from baseline (week-1) were calculated. The weekly scores for changes were further averaged every 4 wk. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs week-1 group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 between groups.
-
Citation: Kondo J, Xiao JZ, Shirahata A, Baba M, Abe A, Ogawa K, Shimoda T. Modulatory effects of
Bifidobacterium longum BB536 on defecation in elderly patients receiving enteral feeding. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(14): 2162-2170 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i14/2162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2162