Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2013; 19(13): 2044-2052
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044
Published online Apr 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044
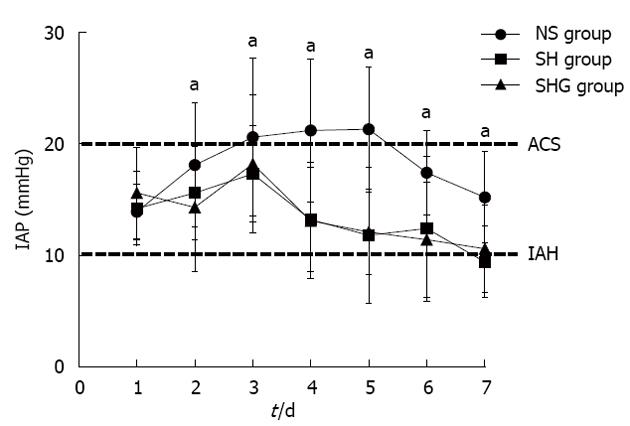
Figure 1 Effect of different resuscitation fluids on changes in intra-abdominal pressure in severe acute pancreatitis.
Intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) was indirectly measured via a bladder catheter during 7 d and performed twice daily. All of the patients had intra-abdominal hypertension on d 1 (IAP > 10 mmHg). aP < 0.05 vs normal saline (NS group). SH group: Combination of normal saline and hydroxyethyl starch; SHG group: Combination of normal saline, hydroxyethyl starch and glutamine; ACS: Abdominal compartment syndrome; IAH: Intra-abdominal hypertension.
- Citation: Zhao G, Zhang JG, Wu HS, Tao J, Qin Q, Deng SC, Liu Y, Liu L, Wang B, Tian K, Li X, Zhu S, Wang CY. Effects of different resuscitation fluid on severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(13): 2044-2052
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i13/2044.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044