Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2013; 19(11): 1736-1748
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1736
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1736
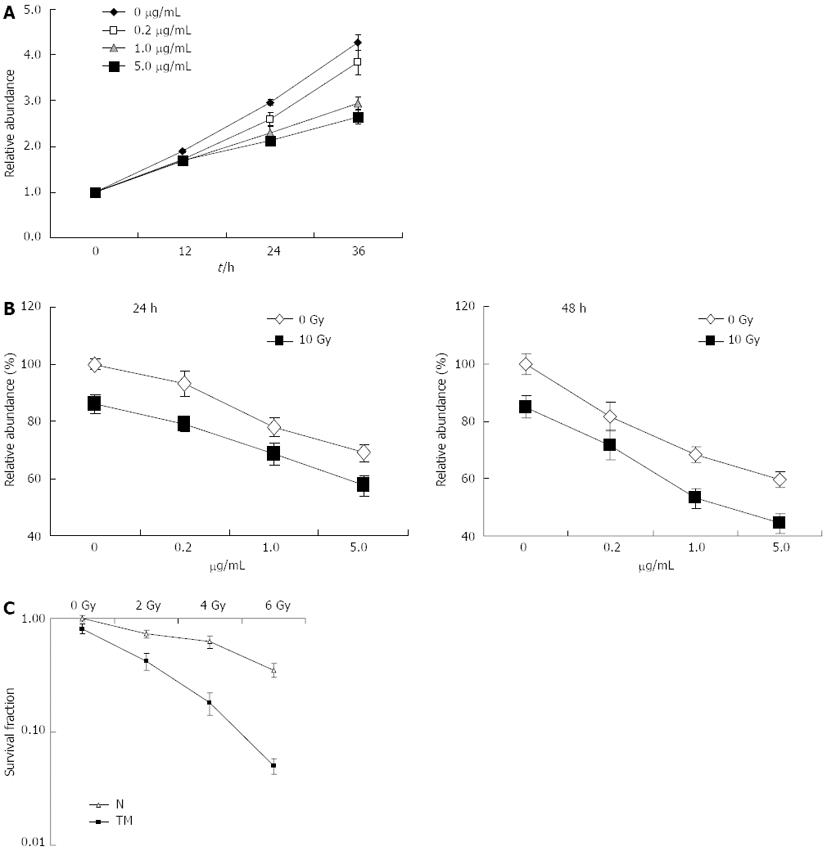
Figure 1 Radiosensitization effect of tunicamycin in EC109 cells.
A: Exponentially growing EC109 cells were treated with tunicamycin (TM) at the indicated concentrations. Cell growth was determined using cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and relative growth rate was calculated using the absorption at 0 h as a baseline; B: EC109 cells were pretreated with or without TM (5 μg/mL), followed by a single dose of 10 Gy. 24 h (left panel) or 48 h (right panel) later, relative cell viability was measured using CCK-8; C: EC109 cells were pretreated with or without TM (5 μg/mL) for 24 h. After irradiation with 2, 4 and 6 Gy, cells were further cultivated for 10-14 d. The number of colonies with > 50 cells was counted under a dissecting microscope. N: Untreated with TM.
- Citation: Pang XL, He G, Liu YB, Wang Y, Zhang B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensitizes human esophageal cancer cell to radiation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(11): 1736-1748
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i11/1736.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1736