Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2013; 19(11): 1718-1727
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718
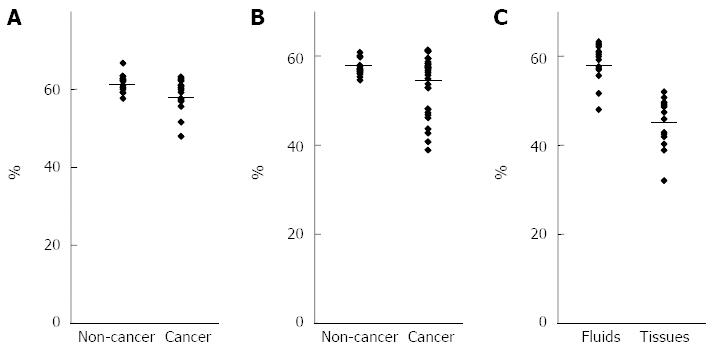
Figure 2 Analysis of long interspersed nuclear element-1 methylation levels using pancreatobiliary fluids.
A: Comparison of the long interspersed nuclear element-1 (LINE-1) methylation levels in pancreatic fluids between pancreatic cancer and noncancerous pancreatic disease; B: Comparison of the LINE-1 methylation levels in biliary fluids between pancreatobiliary cancer and noncancerous pancreatobiliary disease; C: Comparison of the LINE-1 methylation levels in pancreatic cancer between pancreatic fluids and tissues.
- Citation: Kato N, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Ohashi H, Taniguchi H, Suzuki H, Nakazawa M, Kaneto H, Sasaki S, Imai K, Shinomura Y. Cancer detection by ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1 methylation in pancreatobiliary fluids. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(11): 1718-1727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i11/1718.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718