Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2013; 19(10): 1551-1562
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1551
Published online Mar 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1551
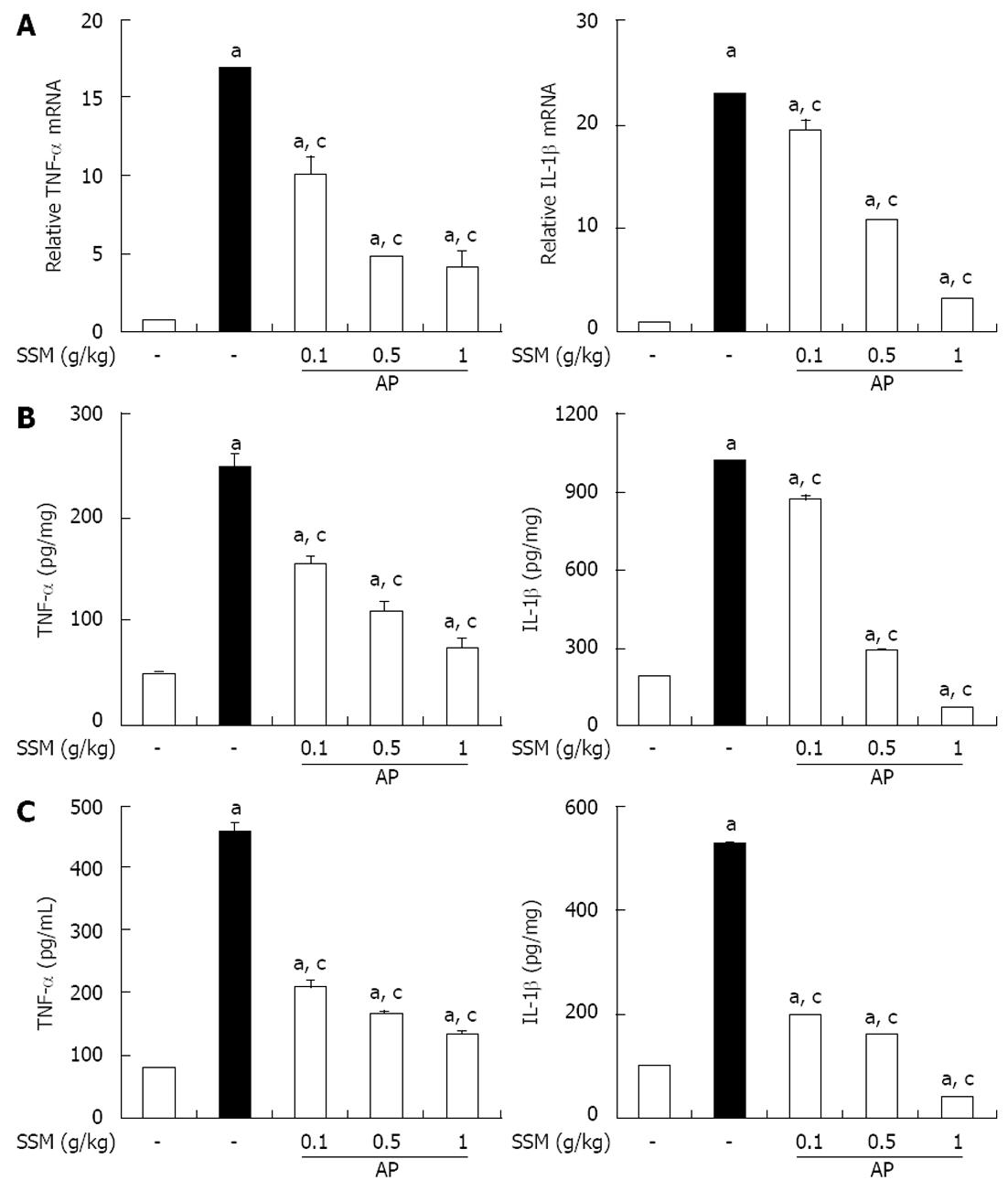
Figure 3 Effect of Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans on tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukins-1β during cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis.
Mice pretreated with Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans (SSM) (0.1, 0.5, or 1 g/kg) were challenged with intraperitoneal injections of cerulein at a supramaximal dose (50 μg/kg). Mice were sacrificed 6 h after the last cerulein injection. A-C: Levels of pancreatic tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β mRNA were quantified by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (A) and the corresponding protein levels were measured in the pancreatic tissue (B) and serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (C). Data are represented as mean ± SE (n = 6 in each group). The results were similar in 3 further experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control group, cP < 0.05 vs cerulein treatment alone. AP: Acute pancreatitis.
-
Citation: Jo IJ, Bae GS, Park KC, Choi SB, Jung WS, Jung SY, Cho JH, Choi MO, Song HJ, Park SJ.
Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans protected the cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis by inhibiting high-mobility group box protein-1. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(10): 1551-1562 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i10/1551.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1551