Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2013; 19(1): 35-41
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.35
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.35
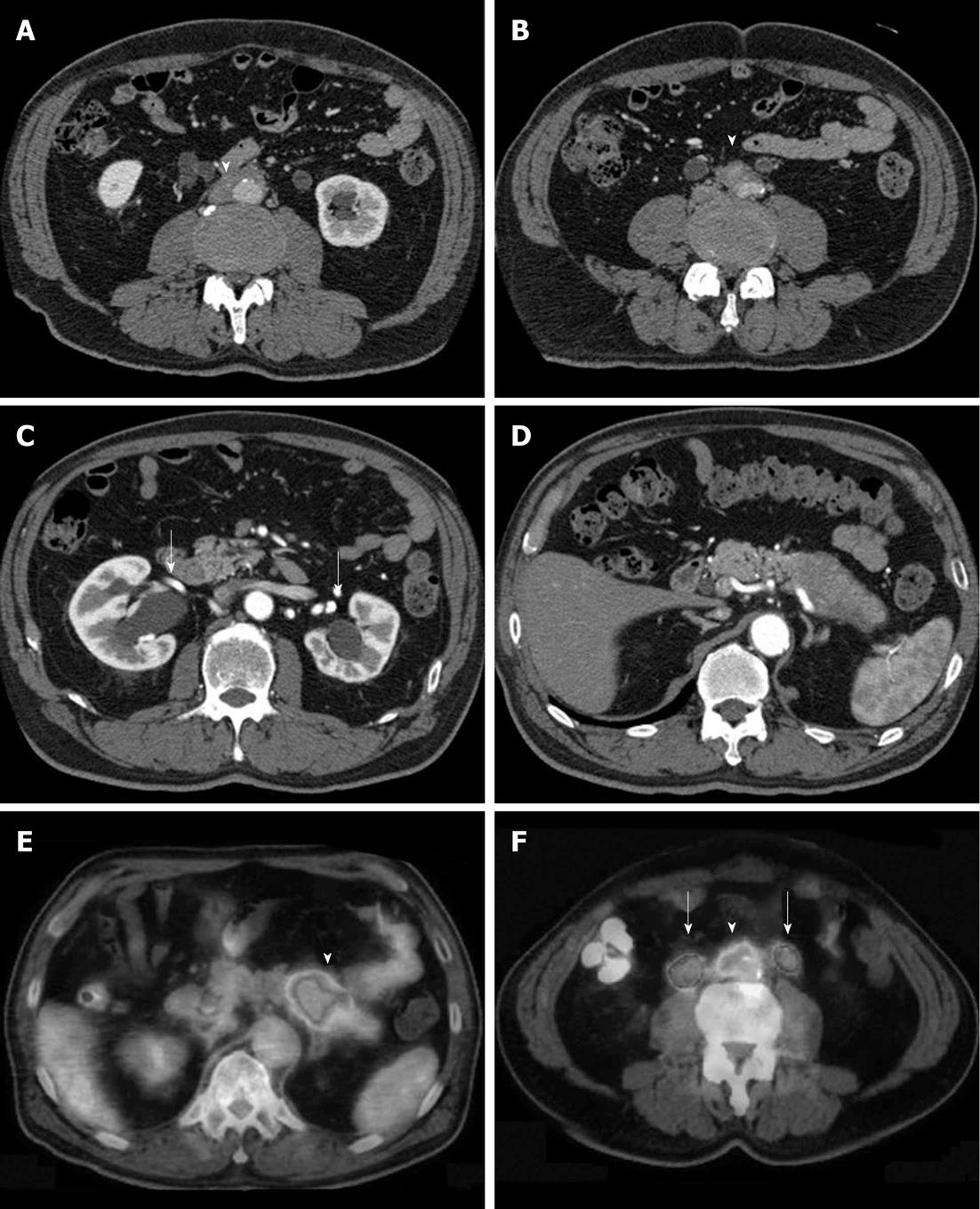
Figure 1 Typical retroperitoneal fibrosis associated with autoimmune pancreatitis.
A, B: Soft tissue (arrow) surrounds the abdominal aorta and common iliac artery; C: Bilateral hydronephrosis (arrows); D: Swelling and capsule-like rim are seen in the body and tail of the pancreas. This case was diagnosed as autoimmune pancreatitis; E, F: Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography images from the same patient; high fluorodeoxyglucose uptake is seen in the body and tail of the pancreas (arrowhead) and in the retroperitoneal fibrosis lesions (arrowhead) surrounding the common iliac artery (arrows indicate dilated urinary ducts).
- Citation: Fujimori N, Ito T, Igarashi H, Oono T, Nakamura T, Niina Y, Hijioka M, Lee L, Uchida M, Takayanagi R. Retroperitoneal fibrosis associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(1): 35-41
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i1/35.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.35