Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2013; 19(1): 133-136
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.133
Published online Jan 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.133
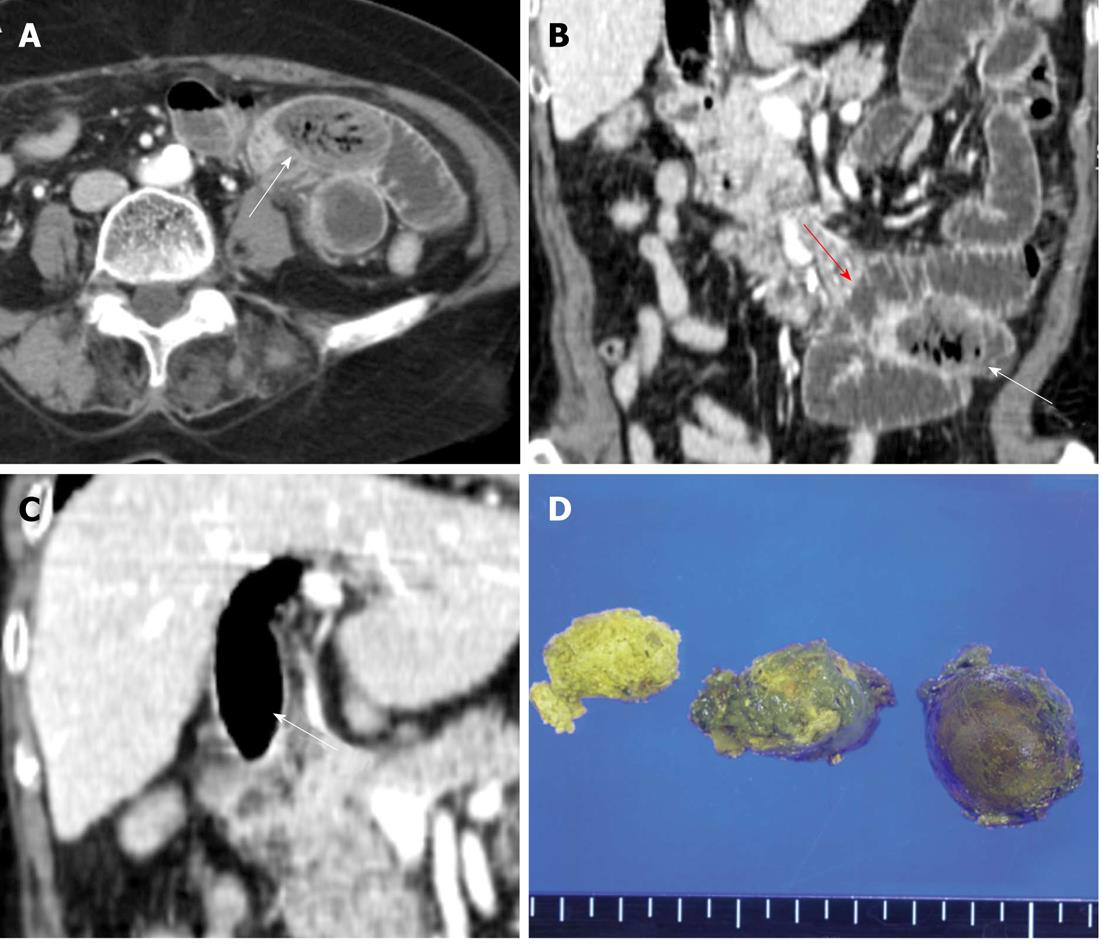
Figure 2 Migration of the biliary phytobezoar resulting in mechanical obstruction of the jejunum.
A and B: Axial portal venous computed tomography and coronal reformatted image at admission showed the migration of the ovoid intraluminal mass (white arrows) with mottled gas pattern to the jejunal loop, as well as a dilated proximal loop (red arrow) containing air-fluid levels suggestive of obstruction; C: Empty extrahepatic bile duct (white arrow) with extensive residual pneumobilia after migration of the bezoar; D: Gross specimen and cut surface of the biliary bezoar.
- Citation: Kim Y, Park BJ, Kim MJ, Sung DJ, Kim DS, Yu YD, Lee JH. Biliary phytobezoar resulting in intestinal obstruction. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(1): 133-136
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i1/133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i1.133