Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2012; 18(9): 952-959
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.952
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.952
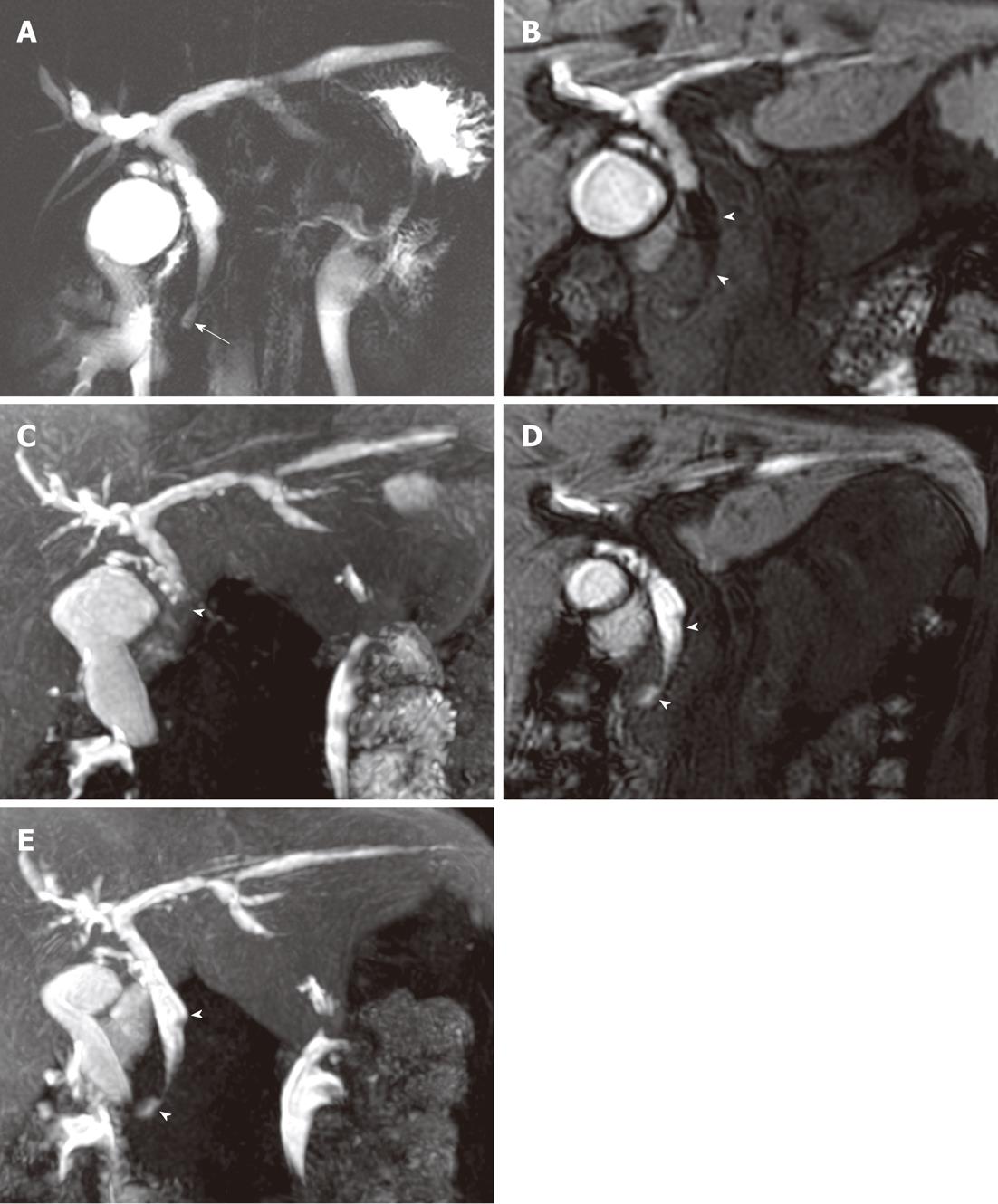
Figure 3 A 40-year-old woman with anomalous union of the pancreatico-biliary duct and a type Ic choledochal cyst.
A: T2-magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC) shows a long common channel (arrow), with diffuse bile duct dilation; B: Sixty-minute delayed gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRC coronal image; C: Maximum intensity projection (MIP) reconstruction image show a filling defect (arrow heads) in the central portion of the distal common bile duct (CBD); D: Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRC coronal images taken 30 min after a fatty meal; E: MIP reconstruction images show a decreased filling defect (arrow heads) in the distal CBD, indicative of pancreatico-biliary reflux.
- Citation: Yeom SK, Lee SW, Cha SH, Chung HH, Je BK, Kim BH, Hyun JJ. Biliary reflux detection in anomalous union of the pancreatico-biliary duct patients. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(9): 952-959
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i9/952.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.952