Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2012; 18(9): 923-929
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.923
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.923
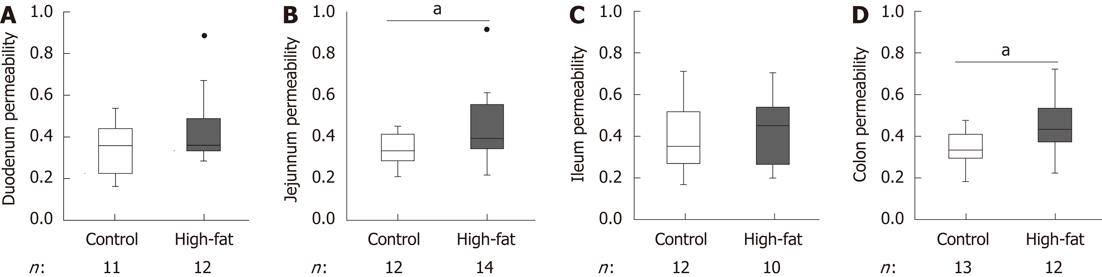
Figure 1 Effect of high-fat-feeding on intestinal permeability.
Intestinal permeability in duodenum (A), jejunum (B), ileum (C), and colon (D) of high-fat-fed vs control mice. Permeability was measured in an Ussing chamber. Results are shown as per mille translocated dextran. Box plots show median, upper and lower quartiles, and Tukey’s whiskers (highest and lowest values, outliers shown as black dots). aP < 0.05 between high-fat and control.
- Citation: Stenman LK, Holma R, Korpela R. High-fat-induced intestinal permeability dysfunction associated with altered fecal bile acids. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(9): 923-929
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i9/923.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.923