Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2012; 18(8): 785-793
Published online Feb 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i8.785
Published online Feb 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i8.785
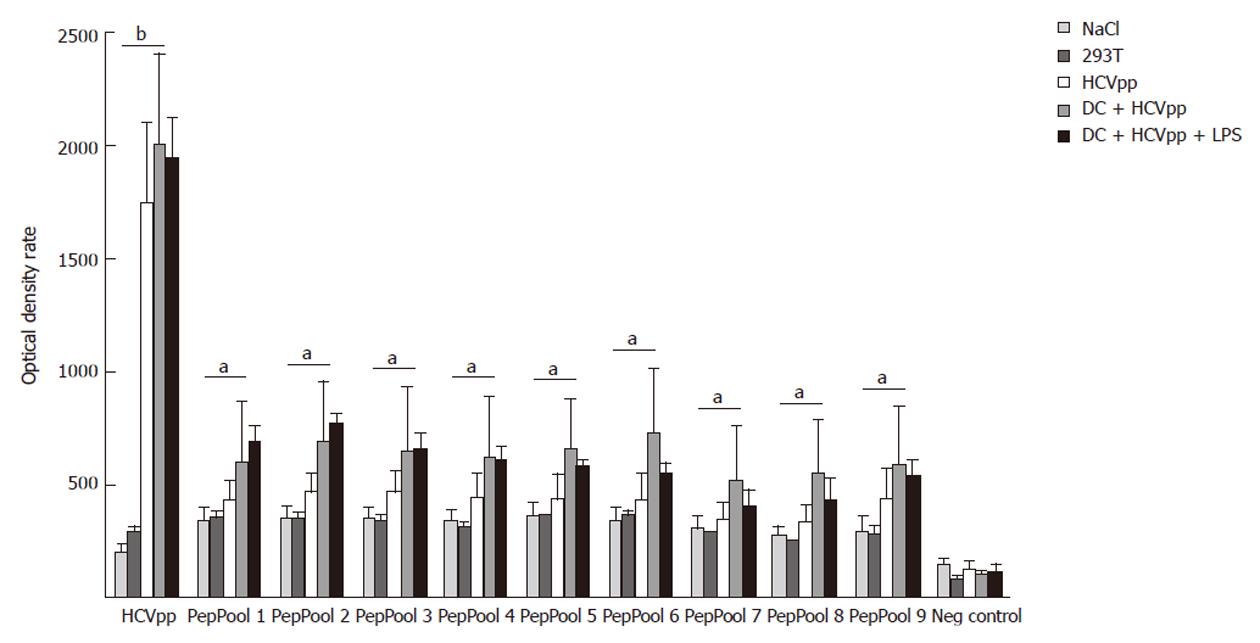
Figure 2 Induction of anti-E1 and anti-E2 antibodies following s.
c. immunization of BALB/c mice. All animals specifically vaccinated developed specific antibodies. Highest antibody titers were observed in the two groups of mice which received the dendritic cell (DC) based vaccines. The negative control with phosphate buffered saline showed only very little unspecific binding. PepSets™ Pools 1-9 spanning the E1 and E2 protein of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) Con1 isolate showed considerably lower binding activity in the treatment groups, whereas the negative control groups did not show any differences between the different antigens. Through serial dilutions OD was calculated for HCV pseudo particles (HCVpp) group to be OD 1755, for the DC + HCVpp group OD 2013 and for the DC + HCVpp+ lipopolysaccharide (LPS) group OD 1944. For significance, NaCl groups were compared with DC + HCVpp groups. Pool 1-3 covers most of the E1 protein, pool 4 comprises the last 24 amino acids of the E1 protein and the first 32 amino acids of the E2 protein, and pool 5-9 enclose the rest of the E2 protein. NaCl: Saline; 293T: Cell culture supernatant of 293T-cells. Results are given as means of quadruplicate measurements of eight mice each group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001.
- Citation: Weigand K, Voigt F, Encke J, Hoyler B, Stremmel W, Eisenbach C. Vaccination with dendritic cells pulsed with hepatitis C pseudo particles induces specific immune responses in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(8): 785-793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i8/785.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i8.785