Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2012; 18(7): 679-684
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.679
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.679
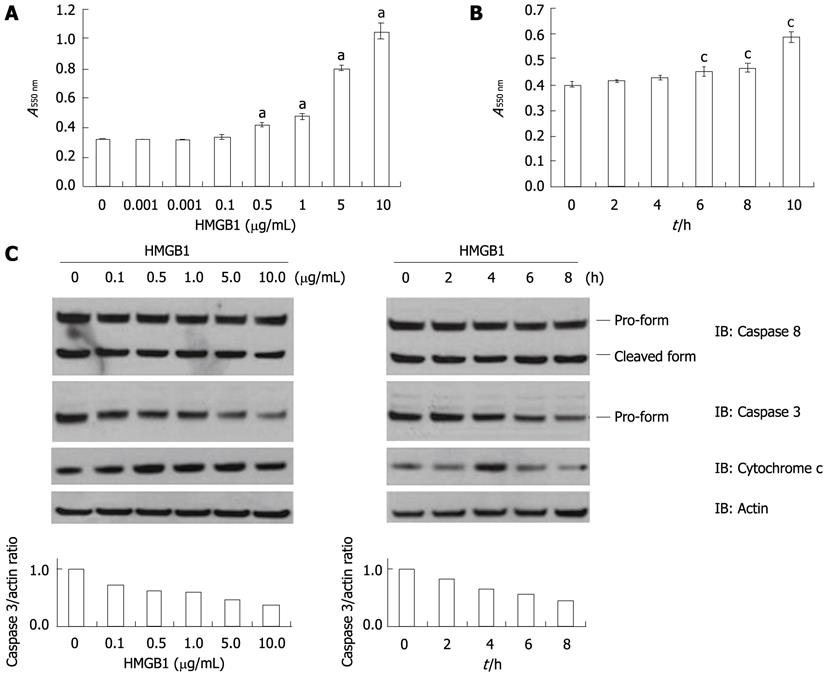
Figure 1 High-mobility group box 1 enhances hepatocyte apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway.
A: Huh-BAT cells were treated with high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) (0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5 and 10 μg/mL) for 6 h. Apoptosis was quantified using an APO Percentage apoptosis assay kit. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three individual experiments. aP < 0.05, vs HMGB1 0 μg/mL; B: Huh-BAT cells were treated with 10 μg/mL of HMGB1 for the indicated time periods. cP < 0.05, vs 0 h; C: Huh-BAT cells were treated with HMGB1 (0 μg/mL, 0.1 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL, 1, 5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL) for 6 h (left column), or with 10 μg/mL of HMGB1 for the indicated time periods (right column). Cells were lysed at the indicated time points, and immunoblot analysis was performed using anti-caspase 8 and anti-caspase 3 antibodies. Mitochondrial and cytosolic extracts were also isolated, and equivalent amounts of cytosolic protein were immunoblotted with an anti-cytochrome c antibody. Immunoblot analysis using an anti-actin antibody was performed as a control for protein loading.
- Citation: Gwak GY, Moon TG, Lee DH, Yoo BC. Glycyrrhizin attenuates HMGB1-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the p38-dependent mitochondrial pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(7): 679-684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i7/679.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.679