Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2012; 18(7): 654-661
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.654
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.654
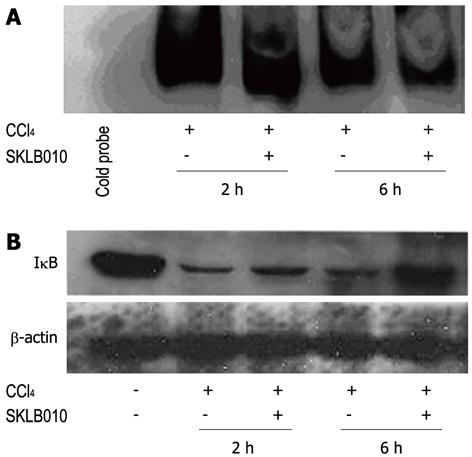
Figure 3 SKLB010 prevented the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB by inhibiting degradation of IκB.
A: The inhibition of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-DNA binding. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-mediated activation of NF-κB resulted in an increase in DNA-binding activity of NF-κB within 2 h, followed by inactivation of NF-κB at 6 h after stimulation which was demonstrated by a lower DNA-binding activity; B: SKLB010 inhibited the CCl4-induced degradation of IκB. Total tissue proteins were analyzed by Western blotting at different time points for IκB-α using specific IκB antibodies. β-actin was used as an internal control.
- Citation: Chen ZZ, Wang ZL, Deng CY, Zheng H, Wang XH, Ma L, Ye X, Ma YH, Xie CF, Chen LJ, Wei YQ. (Z)-5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione protects rats from carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and fibrogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(7): 654-661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i7/654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.654