Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2012; 18(7): 627-636
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.627
Published online Feb 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.627
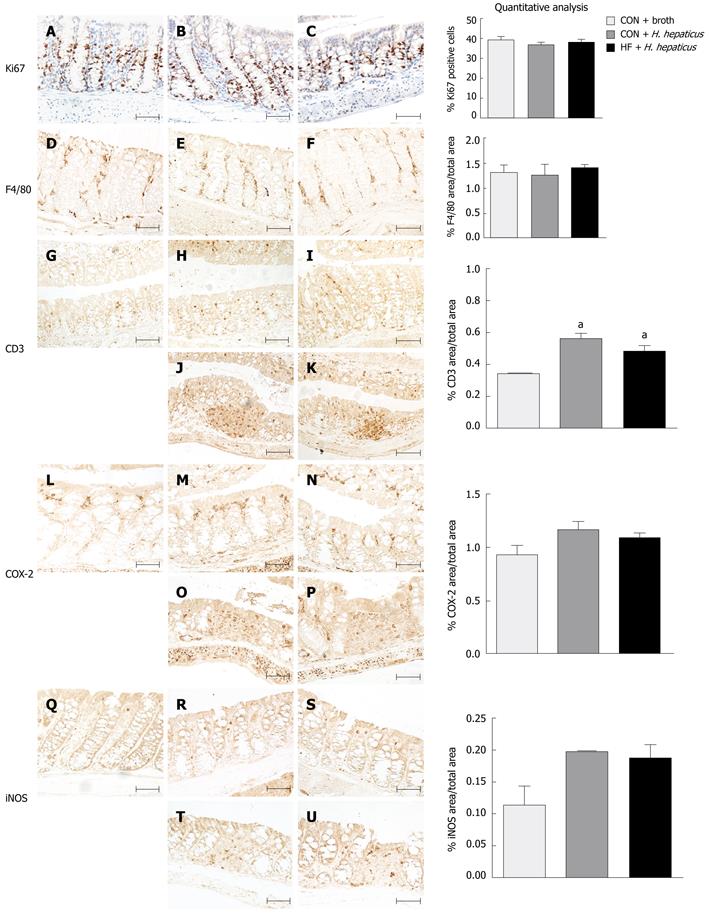
Figure 4 Effect of diet on proliferation and inflammatory markers following infection with Helicobacter hepaticus in SMAD3-/- mice.
Immunohistochemical staining for Ki-67 (A-C), F4/80 (D-F), CD3 (G-K), COX-2 (L-P) and iNOS (Q-U) in proximal colon sections of SMAD3-/- mice fed control (CON) diet and treated with broth (A, D, G, L, Q), CON-fed mice treated with Helicobacter hepaticus (H. hepaticus) (B, E, H, J, M, O, R, T), or fed a high fat (HF) diet and treated with H. hepaticus (C, F, I, K, N, P, S, U) 4 wk post-infection. Normal appearing proximal colon segments (A-I, L-N, Q-S) and inflamed colon segments with lymphoid infiltrate (J, K, O, P, T, U). Scale bars represent 100 μm. There were no significant differences in proliferation indices or in macrophage infiltration. CON and HF diet mice had slightly increased staining for CD3+ T lymphocytes, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) post-infection compared to broth-treated controls, but averages were not statistically significant between diets (P > 0.05). aP < 0.05 vs CON animals.
- Citation: McCaskey SJ, Rondini EA, Langohr IM, Fenton JI. Differential effects of energy balance on experimentally-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(7): 627-636
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i7/627.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.627