Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2012; 18(6): 522-531
Published online Feb 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522
Published online Feb 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522
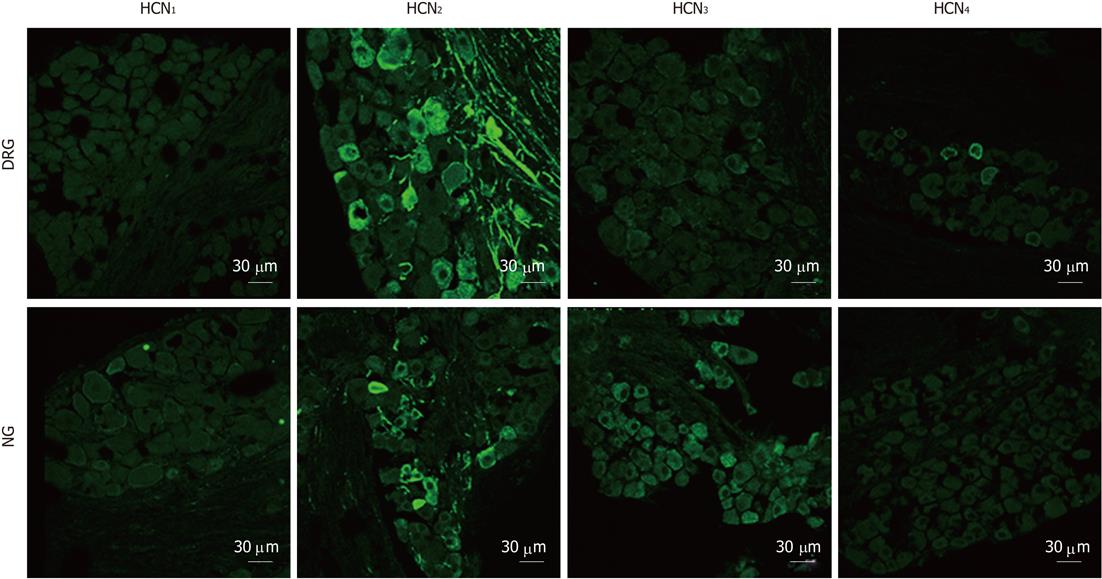
Figure 6 Immunostaining for hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation isoforms in dorsal root ganglia and nodose ganglia sections.
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel 1 (HCN1) immunoreactivity was not detectable in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and nodose ganglia (NG) neurons. HCN2 immunoreactivity was prominent in DRG (cell bodies and fibers) and was also present in some NG neurons and fibers. HCN3 immunoreactivity was profuse in NG sections but was weaker in DRG sections. HCN4 immunoreactivity was present in a minority of DRG neurons and was absent in NG.
- Citation: Wang YP, Sun BY, Li Q, Dong L, Zhang GH, Grundy D, Rong WF. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel subtypes differentially modulate the excitability of murine small intestinal afferents. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(6): 522-531
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i6/522.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522