Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2012; 18(6): 522-531
Published online Feb 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522
Published online Feb 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522
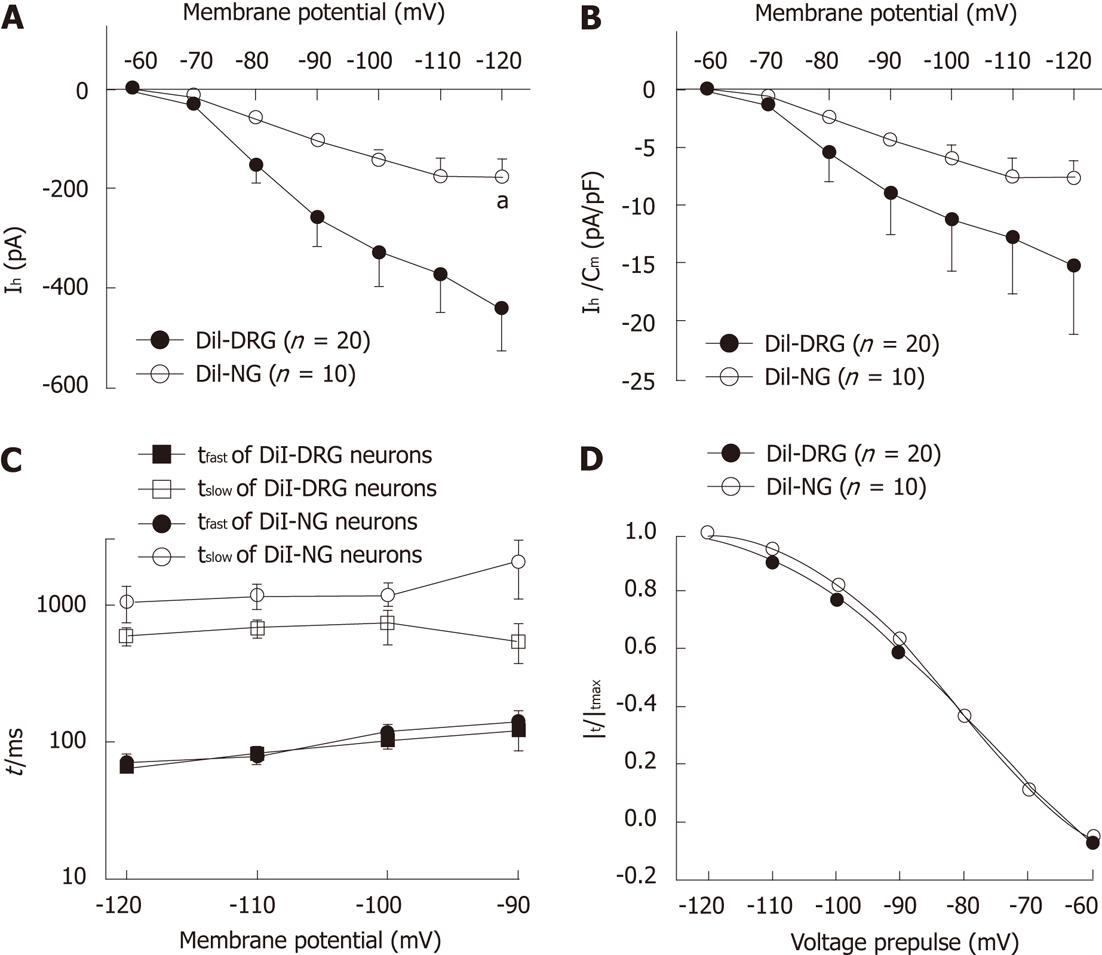
Figure 4 Ih steady-state parameters and activation kinetics in DiI-labeled DRG and NG neurons.
A: Ih current-voltage relationship between DiI-labeled dissociated dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and nodose ganglia neurons (NG); B: Ih current density-voltage relationship between DiI-labeled DRG and NG neurons; C: The time constant of Ih current. Ih current traces were fitted with two exponentials according to the following equation: Ih(t) = Af exp(-t/τf) + As exp(-t/τs), where Ih(t) is the amplitude of the current at time t and Af and As are the initial amplitudes of the fast (τf) and slow (τs) activation time constant components, respectively. Time constants were obtained by fitting currents using pCLAMP; D: Ih current activation curves. Normalized activation curves were obtained from tail currents at -80 mV and fitted by Boltzmann function: Ih/Ih(max) =1/{1+ exp[(Vm – V1/2)/k]}, where Ih is the peak amplitude of the tail current recorded immediately after the pre-pulse, Ih(max) is the maximal current recorded after the maximal prepulse of -120 mV, Vm is the membrane potential, V1/2 is the membrane potential at which Ih conductance is half-activated, and k is a slope factor of the curve. Data were expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs DiI-labeled DRG neurons.
- Citation: Wang YP, Sun BY, Li Q, Dong L, Zhang GH, Grundy D, Rong WF. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel subtypes differentially modulate the excitability of murine small intestinal afferents. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(6): 522-531
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i6/522.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i6.522