Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2012; 18(5): 472-478
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.472
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.472
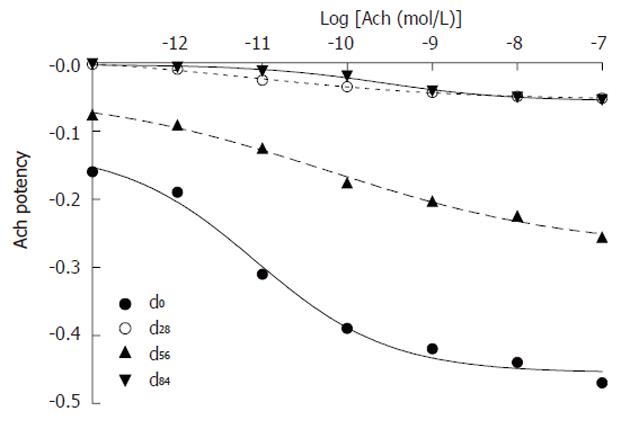
Figure 4 Acetylcholine reduces portal pressure (mean ± SE, ni = 4).
The dose-effect relationship between Acetylcholine and portal vein relaxation in isolated portal perfused rat livers without chronic hepatitis, where rats were administered 3 mL/kg olive oil subcutaneously twice per week for 84 d (control rats) (d0). Rats with chronic hepatitis at three stages, hepatic degeneration (d28), fibrosis (d56) and cirrhosis (d84), were administered 3 mL/kg 40% (v/v) CCl4 in olive oil subcutaneously twice per week for 28 d, 56 d and 84 d, respectively. Ach: Acetylcholine.
- Citation: Zhang T, Xu XY, Zhou H, Zhao X, Song M, Zhang TT, Yin H, Li T, Li PT, Cai DY. A pharmacodynamic model of portal hypertension in isolated perfused rat liver. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(5): 472-478
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i5/472.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.472