Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2012; 18(48): 7184-7193
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7184
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7184
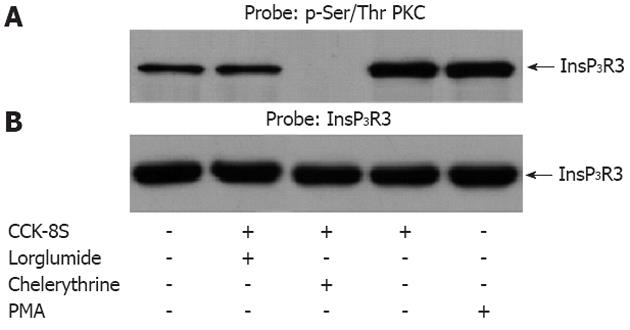
Figure 5 Sulfated cholecystokinin-8 stimulation of interstitial cells of Cajal resulted in the protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of type III inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor.
A: Western blots of proteins were immunoprecipitated with type III inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (InsP3R3)-specific antibody. The immunoprecipitated proteins were probed with antibody specific for phosphorylated Ser/Thr protein kinase C (PKC) substrate sequences. The sulfated cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8S)-induced phosphorylation of InsP3R3 was apparently inhibited by pretreatment with chelerythine. Pretreatment with lorglumide (5 μmol/L) could significantly reduce the CCK-8S intensified phosphorylation of InsP3R3. In the positive control group, treatment of cells with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) also resulted in an enhanced phosphorylation of InsP3R3; B: The nitrocellulose membrane in A was stripped and reprobed with InsP3R3 (1:1000) to determine the levels of InsP3R3 immunoprecipitated. Each cell sample contained nearly equal amounts of InsP3R3.
- Citation: Gong YY, Si XM, Lin L, Lu J. Mechanisms of cholecystokinin-induced calcium mobilization in gastric antral interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(48): 7184-7193
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i48/7184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7184