Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2012; 18(48): 7158-7165
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158
Published online Dec 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158
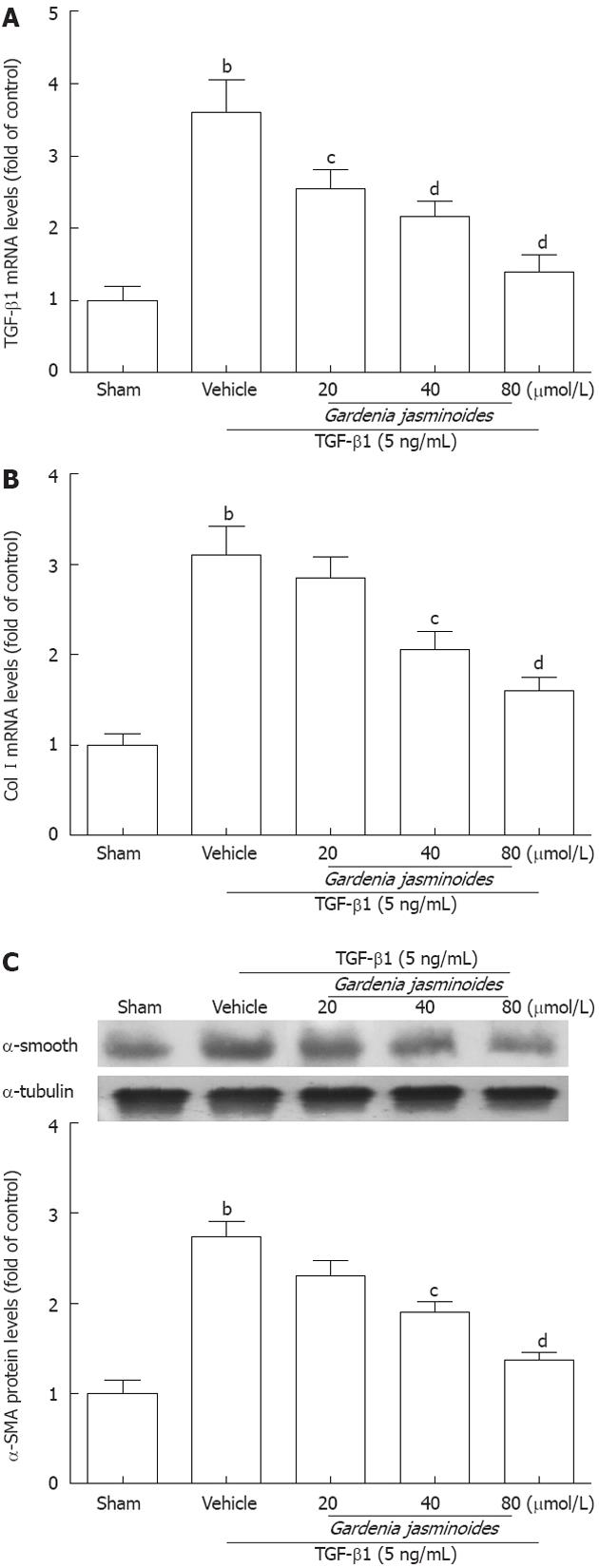
Figure 3 Gardenia jasminoides significantly reduced the expression of fibrotic marker genes in a human hepatic stellate cells line.
Cells were exposed to transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (5 ng/mL) in combination with the indicated concentrations of Gardenia jasminoides or vehicle for 24 h. A: mRNA expression of TGF-β1 in LX-2 cells; B: mRNA expression of collagen type I(Col I) in LX-2 cells; C: Western blotting analysis of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression in LX-2 cells. bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TGF-β1 + vehicle (n = 3).
-
Citation: Chen YH, Lan T, Li J, Qiu CH, Wu T, Gou HJ, Lu MQ.
Gardenia jasminoides attenuates hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in bile duct-ligated rats and human hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(48): 7158-7165 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i48/7158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7158