Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2012; 18(46): 6701-6708
Published online Dec 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6701
Published online Dec 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6701
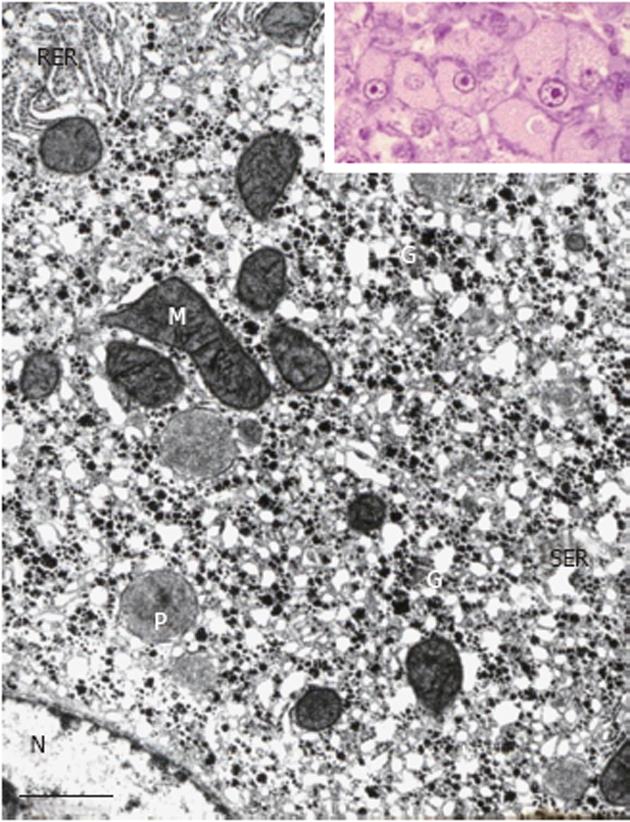
Figure 2 Portion of a glycogenotic acidophilic hepatocyte (corresponding to glycogen-ground-glass hepatocyte) induced in rat liver by N-nitrosomorpholine.
Note abundant α- and β-glycogen particles (G) in close spatial relationship with large network complexes of proliferated smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), mitochondria (M), peroxisomes (P), and nucleus (N). Inset: Group of acidophilic hepatocytes as seen under the light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy, lead citrate. Bar: 1 μm.
- Citation: Bannasch P. Glycogenotic hepatocellular carcinoma with glycogen-ground-glass hepatocytes: A heuristically highly relevant phenotype. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(46): 6701-6708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i46/6701.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6701