Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2012; 18(45): 6635-6644
Published online Dec 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6635
Published online Dec 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6635
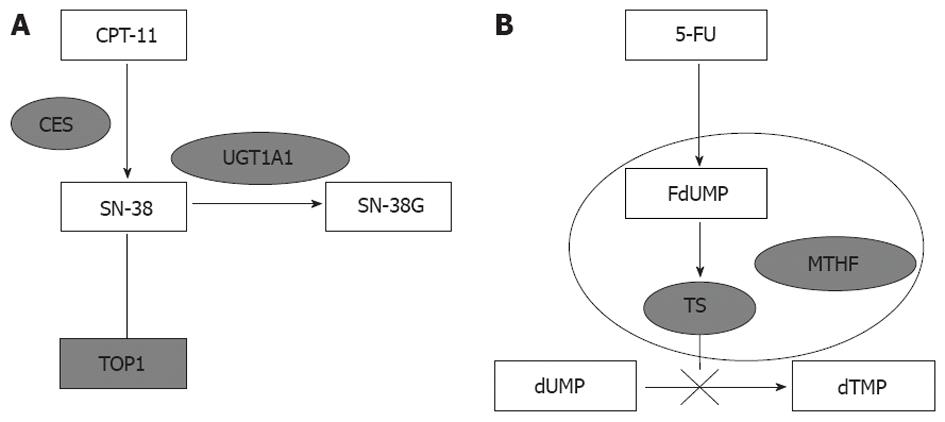
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase1A1 and thymidylate synthetase.
A: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase1A1 (UGT1A1) is the main enzyme involved in the glucuronidation of SN-38 (SN-38G). Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of UGT1A1 are the key factor in irinotecan metabolism; B: Thymidylate synthetase (TS) is the main target of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). The ternary complex of TS, active metabolite of 5-FU (FdUMP) and methyl-tetra-hydrofolic acid (MTHF) inhibits DNA synthesis. SNP of TS affects the expression of enzyme and 5-FU efficacy. CES: Carboxylesterases; TOP1: Topoisomerase-1.
-
Citation: Wang Y, Shen L, Xu N, Wang JW, Jiao SC, Liu ZY, Xu JM.
UGT1A1 predicts outcome in colorectal cancer treated with irinotecan and fluorouracil. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(45): 6635-6644 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i45/6635.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6635