Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2012; 18(44): 6504-6509
Published online Nov 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i44.6504
Published online Nov 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i44.6504
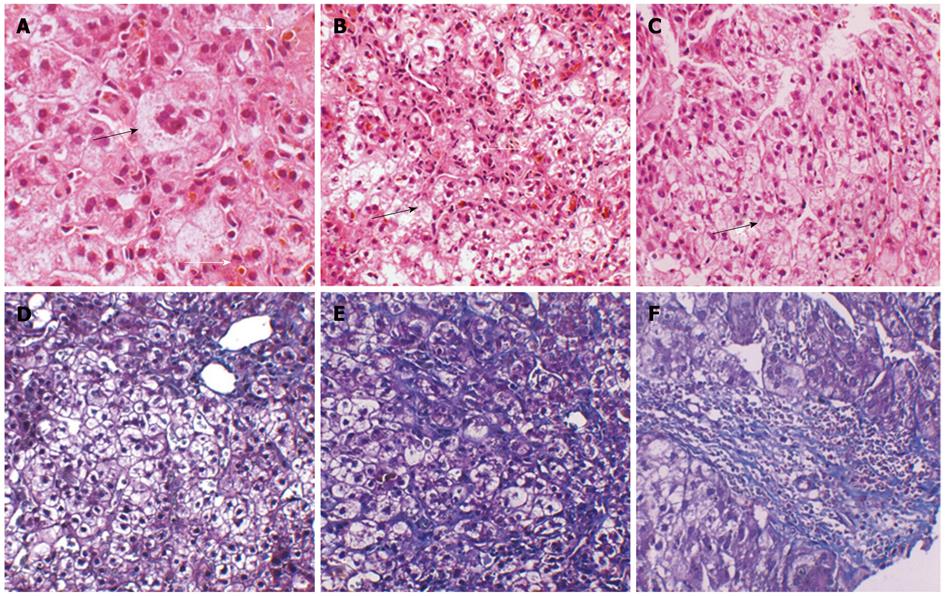
Figure 1 Histological features of samples taken at age 10 and current liver biopsy specimens (age 23 years).
A: Multinucleated giant cells (black arrow) and ductal cholestasis (white arrow) in the previously sampled liver tissue (image, × 400); B: Ductal cholestasis (white arrow) and ballooning degeneration of the hepatocytes (black arrow) in the previously sampled liver tissue (image, × 200); C: Ductal cholestasis and hepatocytes ballooning degeneration (black arrow) in the recently sampled liver tissue (image, × 200); D: Mild portal and lobular fibrosis in the previously sampled liver tissue (image, × 200); E: Moderate lobular fibrosis in the recently sampled liver tissue (image, × 200); F: Moderate portal fibrosis in the recently sampled liver tissue (image, × 200).
-
Citation: Deng BC, Lv S, Cui W, Zhao R, Lu X, Wu J, Liu P. Novel
ATP8B1 mutation in an adult male with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(44): 6504-6509 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i44/6504.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i44.6504