Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2012; 18(43): 6226-6234
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6226
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6226
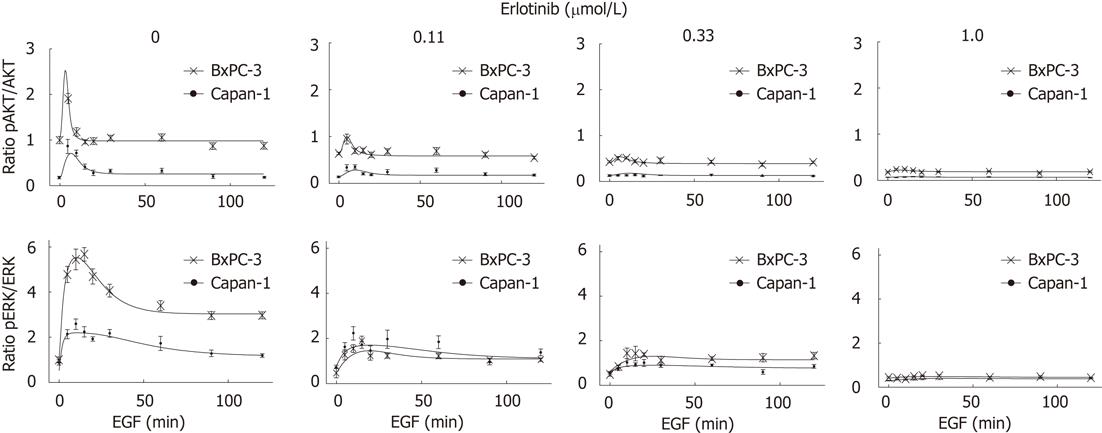
Figure 5 Simulations of the mathematical model reflect the experimental time series.
Serum-starved BxPC-3 and Capan-1 cells were preincubated with different doses of erlotinib for 4 h and stimulated with 10 ng/mL epidermal growth factor (EGF) for the indicated times. Cellular lysates were analyzed by quantitative immunoblotting, and phospho-protein kinase B (pAKT), protein kinase B (AKT), phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase levels were determined. Plotted are experimental results (BxPC-3 and Capan-1); mean ± SE of at least six independent experiments and model simulation (lines) for BxPC-3 and Capan-1 cells for different times of EGF stimulation. All data were scaled to the untreated BxPC-3 cells (absence of EGF and erlotinib), where the ratio was set as 1.
- Citation: Lange F, Rateitschak K, Kossow C, Wolkenhauer O, Jaster R. Insights into erlotinib action in pancreatic cancer cells using a combined experimental and mathematical approach. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(43): 6226-6234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i43/6226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6226