Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6018-6026
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018
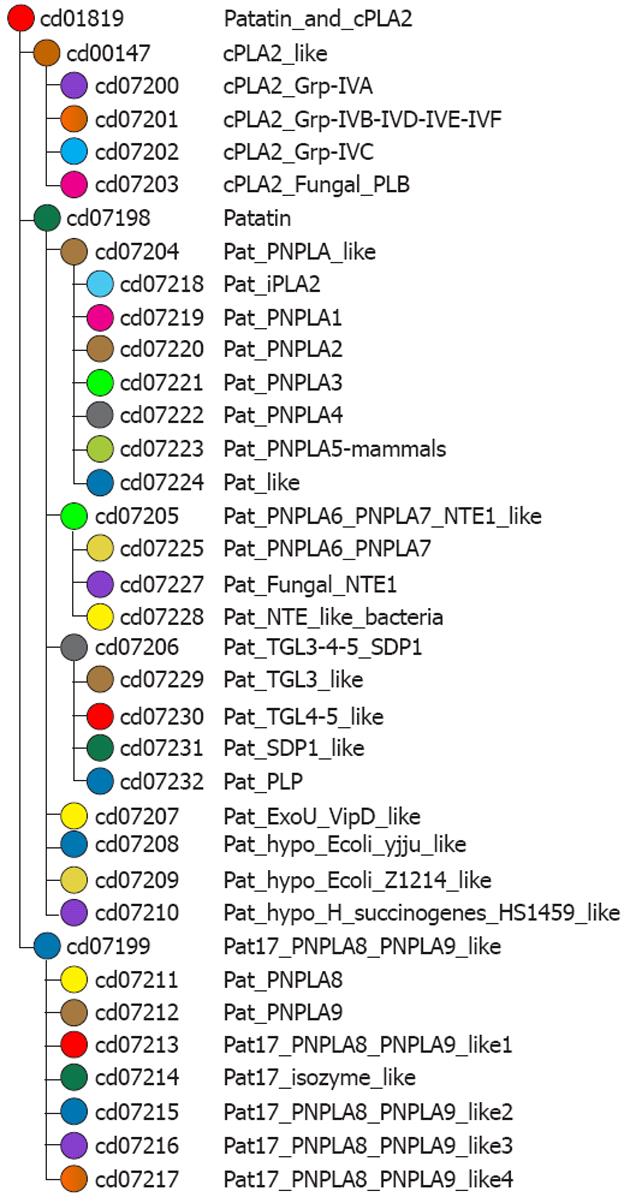
Figure 6 Domain family hierarchy of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 protein.
Data extracted from NCBI-curated domains at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml. This picture provides data about how patterns of residue conservation and divergence in a family relate to functional properties. In this particular case, picture shows the patatin-like phospholipase family. Patatin is a storage protein, but it also has the enzymatic activity of a lipid acyl hydrolase, catalyzing the cleavage of fatty acids from membrane lipids. Members of this family have also been found in vertebrates. This family also includes the catalytic domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (PLA2; EC 3.1.1.4) hydrolyzes the sn-2-acyl ester bond of phospholipids to release arachidonic acid. At the active site, cPLA2 contains a serine nucleophile through which the catalytic mechanism is initiated. PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; TGL: Triglyceride lipase; PLP: Pyridoxal phosphate.
- Citation: Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. PNPLA3, the triacylglycerol synthesis/hydrolysis/storage dilemma, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6018-6026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6018.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018