Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2012; 18(40): 5753-5758
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5753
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5753
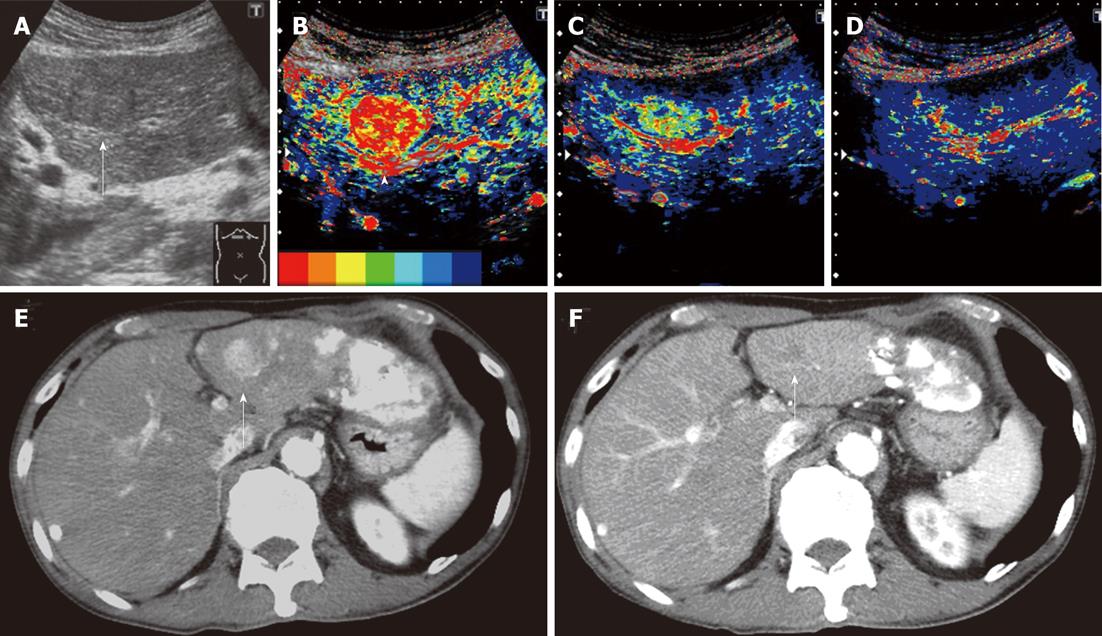
Figure 2 Clinical example of good responder patient.
A 74-year-old man with a history of hepatitis C virus cirrhosis underwent transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma three times, after which sorafenib administration (400 mg/d) was started for this patient because the tumor was TACE-refractory. A: Gray-scale ultrasonography showed a mosaic-pattern tumor sized 20 mm in diameter in S3 (arrow). This tumor was established as a target lesion; B: A large artery near this tumor was regarded as starting point (arrow head). The color mapping (CM) image before the treatment showed primarily red or orange in the tumor; C: The CM image 2 wk after the treatment showed primarily green in the tumor; D: The CM image 4 wk after the treatment showed primarily dark blue in the tumor, the same as the surrounding parenchyma; E: Dynamic computed tomography (CT) scan in arterial phase before the treatment showed a hypervascular lesion in S3 (arrow) which was the target lesion and accumulation of iodized oil in the left lobe and S7; F: Dynamic CT scan in arterial phase 4 wk after the treatment showed a hypovascular lesion in S3 (arrow) and this lesion reduced. This therapeutic response was described as a partial response.
- Citation: Shiozawa K, Watanabe M, Kikuchi Y, Kudo T, Maruyama K, Sumino Y. Evaluation of sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: A pilot study. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(40): 5753-5758
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i40/5753.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5753