Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2012; 18(40): 5719-5728
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5719
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5719
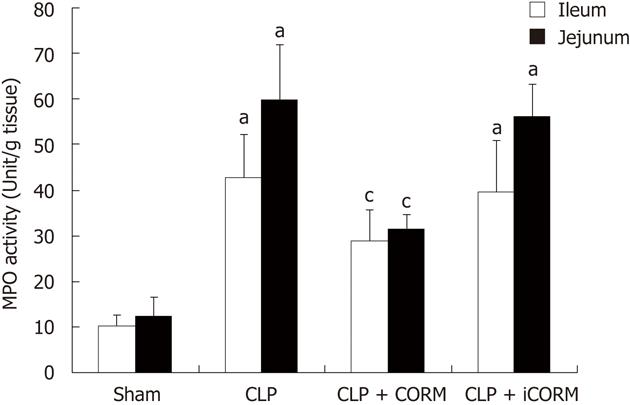
Figure 2 Effects of tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer carbon monoxide-releasing molecules on myeloperoxidase activity in the small intestine of septic mice.
Mice were challenged with cecal ligation and perforation (CLP) and treated with tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the mid-ileum and mid-jejunum were assessed 24 h following CLP injury. Results are mean ± SE, aP < 0.01 vs sham mice; cP < 0.05 vs CLP mice. CORM: Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule; iCORM: Inactivated-carbon monoxide-releasing molecule.
- Citation: Wang X, Cao J, Sun BW, Liu DD, Liang F, Gao L. Exogenous carbon monoxide attenuates inflammatory responses in the small intestine of septic mice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(40): 5719-5728
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i40/5719.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i40.5719