Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2012; 18(4): 302-308
Published online Jan 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i4.302
Published online Jan 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i4.302
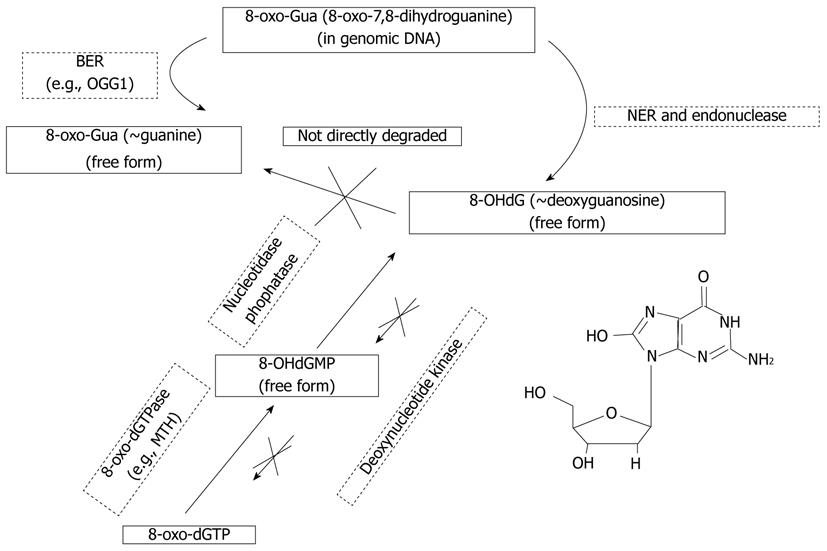
Figure 2 Generation and metabolism of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine.
8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) is a DNA glycosylase enzyme involved in base excision repair (BER), and is the primary enzyme responsible for excision of 7,7-dihydro-8-oxoguanine that occurs as a result of exposure to reactive oxygen species (ROS). OGG1 is a bifunctional glycosylase, because it is able to both cleave the glycosidic bond of the mutagenic lesion, and cause strand breakage in the DNA backbone. Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is a DNA repair mechanism, which is a particularly important mechanism by which the cell can prevent unwanted mutations by removing the vast majority of ROS-induced DNA damage.
- Citation: Ock CY, Kim EH, Choi DJ, Lee HJ, Hahm KB, Chung MH. 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: Not mere biomarker for oxidative stress, but remedy for oxidative stress-implicated gastrointestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(4): 302-308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i4/302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i4.302