Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2012; 18(39): 5622-5631
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5622
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5622
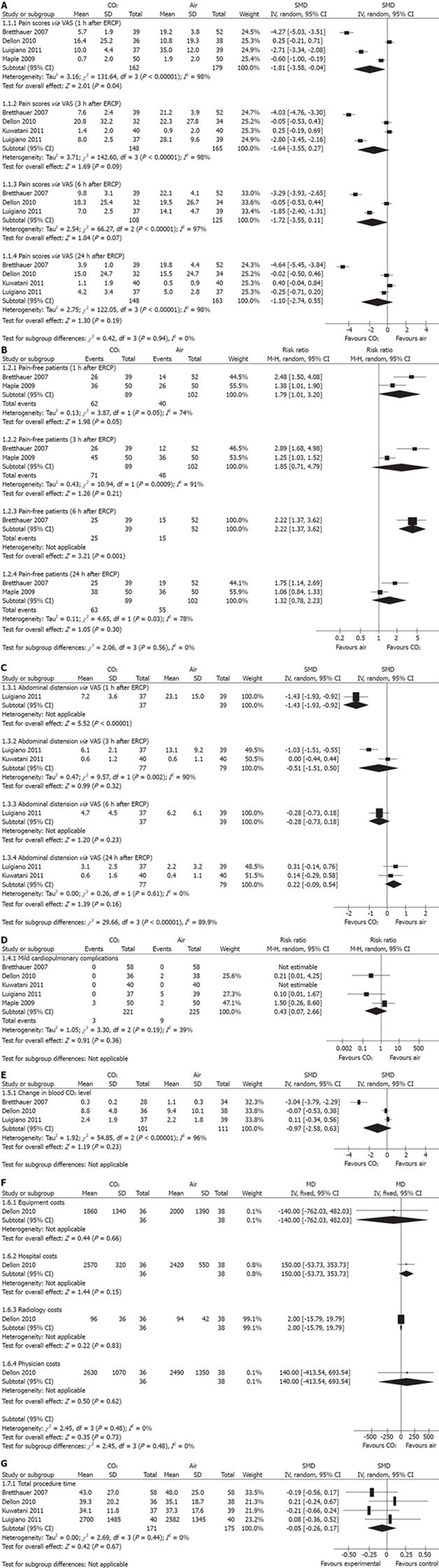
Figure 2 Forest plots of meta-analysis.
A: Carbon dioxide vs air in abdominal pain scores; B: Carbon dioxide vs air in pain-free patients; C: Carbon dioxide vs air in abdominal distension; D: Carbon dioxide vs air in mild cardiopulmonary complications; E: Carbon dioxide vs air in change in blood carbon dioxide level; F: Carbon dioxide vs air in total costs; G: Carbon dioxide vs air in total procedure time. IV: Inverse-variance; M-H: Mantel Haenszel; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; VAS: Visual analogue scale; MD: Mean difference; SMD: Standardized mean difference.
- Citation: Cheng Y, Xiong XZ, Wu SJ, Lu J, Lin YX, Cheng NS, Wu TX. Carbon dioxide insufflation for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(39): 5622-5631
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i39/5622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5622