Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2012; 18(39): 5542-5550
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5542
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5542
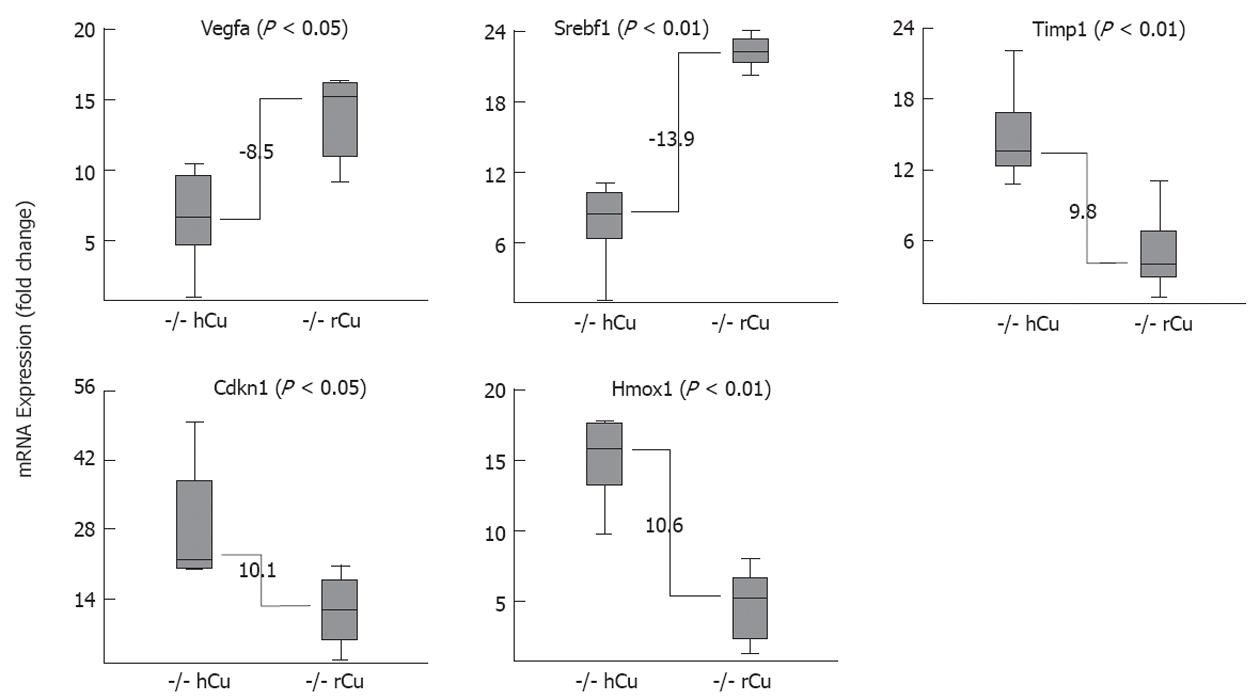
Figure 6 Liver gene expression of Long-Evans cinnamon rat is significantly altered after high copper regimen.
Relative expression of individual mRNA in Long-Evans cinnamon (LEC) rats (n = 7) that were subjected to early high copper (hCu) regimen (left boxes) and in age-matched LEC rats (n = 5) receiving reduced copper (rCu) (right boxes). Animals were analyzed at fulminant hepatitis. Fold-change was calculated within groups by the Δct method using the HPRT gene for normalization. Data are shown as a box plot representation as calculated from three independent experiments. Numbers refer to difference of fold-change with regard to the median of each group.
- Citation: Siaj R, Sauer V, Stöppeler S, Spiegel HU, Köhler G, Zibert A, Schmidt HH. Dietary copper triggers onset of fulminant hepatitis in the Long-Evans cinnamon rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(39): 5542-5550
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i39/5542.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5542