Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5404-5411
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5404
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5404
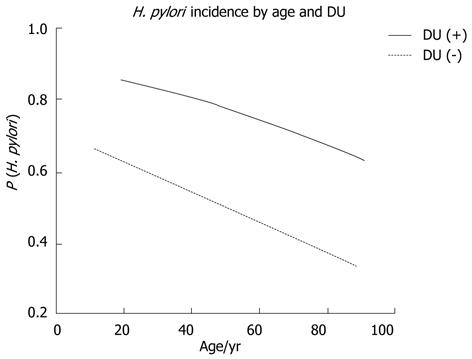
Figure 4 Logistic regression curves of age and duodenal ulcer disease as independent factors to explain Helicobacter pylori incidence.
The model had a highly significant fit (age OR = 0.9827, P < 0.0001; DU OR = 3.6077, P < 0.0001). A posterior test for the age/DU interaction had a nonsignificant result (β3 = 0.0085, SE = 0.0168, P = 0.6142, OR = 1.0085, CI- = 0.9758, CI+ = 1.0423). DU: Duodenal ulcer; OR: Odds ratios; CI: Confidence intervals; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Suzuki RB, Cola RF, Cola LTB, Ferrari CG, Ellinger F, Therezo AL, Silva LC, Eterovic A, Sperança MA. Different risk factors influence peptic ulcer disease development in a Brazilian population. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5404-5411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5404