Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5351-5359
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5351
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5351
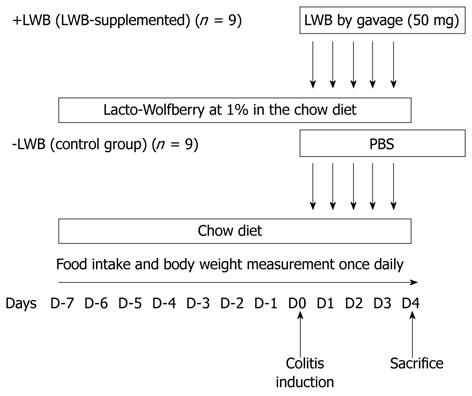
Figure 1 Animal study design.
Body weight and food intake was monitored throughout the duration of the experiment (i.e., D-7 to D4). Colitis was induced on D0. For the Lacto-wolfberry (LWB) fed group, diet was supplemented with 1% LWB from D-7 until D4 and 50 mg of LWB was also gavaged from D0 to D4. Control animals were fed regular diet for the same period and gavaged with equal volume of control solution from D0 to D4. PBS: Phosphate buffered solution.
- Citation: Philippe D, Brahmbhatt V, Foata F, Saudan Y, Serrant P, Blum S, Benyacoub J, Vidal K. Anti-inflammatory effects of Lacto-Wolfberry in a mouse model of experimental colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5351-5359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5351.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5351