Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2012; 18(36): 5122-5128
Published online Sep 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5122
Published online Sep 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5122
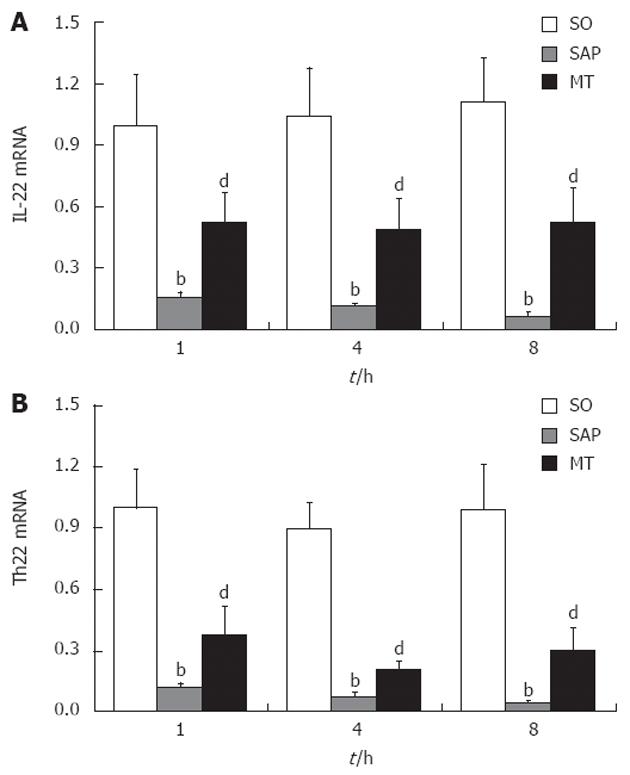
Figure 3 Levels of mRNAs encoding interleukin 22 and T helper cell 22 in lung tissue samples from rats in the sham operation, severe acute pancreatitis, and melatonin treatment groups.
A: Expression of IL-22 mRNA 1, 4 and 8 h after induction of SAP; B: Expression of Th22 mRNA 1, 4 and 8 h after induction of SAP. Levels of mRNAs encoding IL-22 and Th22 decreased with continued progression of SAP (P < 0.01). bP < 0.01 vs the SO group; dP < 0.01 vs the SO and SAP groups (n = 8 rats per group). SO: Sham operation; SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; IL: Interleukin; Th: T helper cell; MT: Melatonin treatment.
- Citation: Huai JP, Sun XC, Chen MJ, Jin Y, Ye XH, Wu JS, Huang ZM. Melatonin attenuates acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury in rats by modulating interleukin 22. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(36): 5122-5128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i36/5122.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.5122